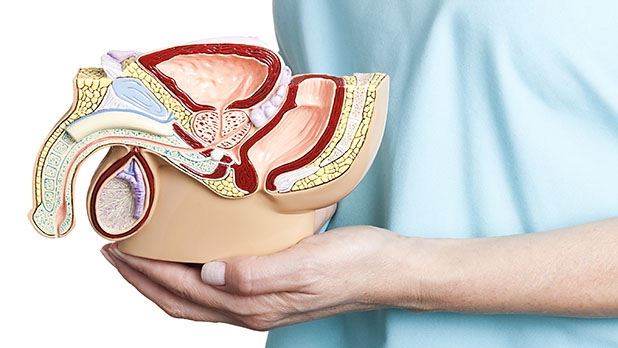
Penile Microsurgical Artery Anastomosis (PMA) is a specialized surgical procedure aimed at treating erectile dysfunction caused by arterial insufficiency.
This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of pricing this procedure in Turkey, a renowned destination for medical tourism due to its quality healthcare infrastructure and competitive pricing.

Understanding the Cost Factors
Surgeon’s Expertise and Reputation
The experience and reputation of the surgeon performing the PMA procedure also influence the pricing. Highly skilled surgeons with extensive experience in microsurgery and urology may charge higher fees. Surgeon fees typically range from $3,000 to $6,000 USD.
Pre-operative Assessments and Tests
Before undergoing PMA surgery, patients require thorough pre-operative assessments and tests to ensure they are suitable candidates. These tests include Doppler ultrasound, blood tests, and consultations with specialists. The cost of these assessments ranges from $500 to $1,000 USD.
Anesthesia and Hospital Stay
Anesthesia fees and hospital accommodation during the PMA procedure are crucial cost components. Anesthesia costs vary depending on the type used (general or local) and typically range from $500 to $1,000 USD. Hospital stay costs can add an additional $1,000 to $2,000 USD per day, depending on the facility.
Prices of all types of the PMA procedure in Turkey.
Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIA) PMA
Definition and Details:
Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIA) PMA is a microsurgical procedure designed to treat erectile dysfunction caused by arterial insufficiency.
This technique involves using the superficial circumflex iliac artery, which runs superficially along the iliac crest, as the donor artery.
The SCIA is carefully dissected and utilized to create a vascular bypass to the penile arteries, circumventing areas of arterial blockage or damage.
By restoring adequate blood flow to the penis, SCIA PMA aims to improve erectile function and enhance overall sexual health.
This procedure requires meticulous surgical skill due to the delicate nature of microsurgical techniques involved in arterial anastomosis.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Patients undergo thorough evaluations including Doppler ultrasound to assess arterial flow, blood tests to evaluate overall health, and consultations with urologists or vascular surgeons to determine candidacy.
- Surgical Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, the surgeon makes precise incisions to access the SCIA. Using advanced microsurgical instruments, the SCIA is carefully dissected and prepared for anastomosis.
- Arterial Anastomosis: Microsurgical techniques are employed to connect the SCIA to the penile arteries, ensuring a precise and secure vascular bypass. This step aims to optimize blood flow to the penis, addressing the underlying arterial insufficiency.
- Post-operative Care: Following surgery, patients require close monitoring in a hospital setting to manage pain, monitor wound healing, and prevent complications. Medications may be prescribed to aid recovery and prevent infection.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Inferior Epigastric Artery (IEA) PMA
Definition and Details:
The Inferior Epigastric Artery (IEA) PMA procedure is a microsurgical approach utilized to treat erectile dysfunction resulting from specific arterial blockages.
The IEA, originating from the external iliac artery, is selected as the donor artery in this technique.
The IEA runs along the inferior aspect of the abdomen and provides a reliable vascular conduit for creating an arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
By bypassing areas of arterial obstruction or damage, IEA PMA aims to restore sufficient blood flow to the penis, thereby improving erectile function and enhancing sexual performance. This procedure requires precise surgical expertise and is tailored to each patient’s anatomical considerations and vascular health.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Extensive evaluations including vascular imaging studies such as Doppler ultrasound, blood tests, and consultations with urologists or vascular surgeons to assess arterial anatomy and determine surgical candidacy.
- Surgical Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, the surgeon carefully identifies and prepares the IEA for harvesting. Microsurgical techniques are employed to isolate the IEA while preserving its integrity and ensuring optimal blood flow characteristics.
- Microsurgical Anastomosis: Using meticulous surgical techniques, the surgeon performs an arterial anastomosis between the IEA and the penile arteries. This step involves precise suturing to create a secure and functional vascular bypass, facilitating improved blood circulation to the penis.
- Post-operative Care: Following surgery, patients require vigilant monitoring in a hospital setting to manage pain, monitor wound healing, and prevent complications such as infection or thrombosis. Post-operative medications may be prescribed to aid recovery and promote optimal healing outcomes.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Radial Artery PMA
Definition and Details:
Radial Artery PMA involves using the radial artery from the forearm as the donor artery for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This procedure is chosen based on the accessibility and size of the radial artery, which can provide sufficient blood flow to the penis.
Radial Artery PMA is typically considered for patients with specific arterial conditions that make this donor artery suitable for creating a vascular bypass to improve erectile function.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Comprehensive evaluations including vascular studies, blood tests, and consultations to assess arterial suitability and overall health.
- Surgical Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, the surgeon harvests the radial artery from the forearm using microsurgical techniques.
- Arterial Anastomosis: The radial artery is meticulously anastomosed to the penile arteries using precise microsurgical suturing techniques to ensure adequate blood flow to the penis.
- Post-operative Care: Patients require hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to facilitate recovery and prevent complications.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Saphenous Vein PMA
Definition and Details:
Saphenous Vein PMA utilizes the great saphenous vein, commonly harvested from the leg, as the donor vessel for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This procedure is suitable for patients with specific arterial insufficiencies where the saphenous vein can serve as a reliable conduit to enhance blood flow to the penis, thereby improving erectile function.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Detailed vascular assessments, imaging studies, and consultations to evaluate arterial anatomy and determine surgical candidacy.
- Surgical Procedure: Under general anesthesia, the surgeon harvests the saphenous vein and prepares it for microsurgical anastomosis.
- Microsurgical Anastomosis: Precise microsurgical techniques are employed to connect the saphenous vein to the penile arteries, ensuring optimal blood flow and function of the vascular bypass.
- Recovery and Follow-up: Post-operative care includes hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to facilitate healing and prevent complications.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Internal Pudendal Artery PMA
Definition and Details:
Internal Pudendal Artery PMA involves utilizing the internal pudendal artery, a branch of the internal iliac artery, as the donor artery for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This technique is selected based on the proximity of the internal pudendal artery to the penile arteries and its ability to provide sufficient blood flow for improving erectile function in patients with specific arterial conditions.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Comprehensive vascular evaluations, including Doppler ultrasound and consultations with specialists, to assess arterial suitability and overall health.
- Surgical Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, the surgeon identifies and prepares the internal pudendal artery using microsurgical techniques.
- Arterial Anastomosis: Precise microsurgical suturing techniques are employed to connect the internal pudendal artery to the penile arteries, creating a vascular bypass to enhance blood flow and erectile function.
- Post-operative Care: Hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to ensure proper healing and recovery.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Deep Circumflex Iliac Artery (DCIA) PMA
Definition and Details:
Deep Circumflex Iliac Artery (DCIA) PMA involves using the deep circumflex iliac artery, which originates from the external iliac artery, as the donor artery for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This procedure is chosen based on the anatomical considerations and arterial characteristics that make the DCIA suitable for creating a vascular conduit to enhance blood flow and improve erectile function.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Comprehensive vascular studies, including imaging and consultations with specialists, to evaluate arterial anatomy and determine surgical suitability.
- Surgical Procedure: Under general anesthesia, the surgeon identifies and prepares the DCIA using precise microsurgical techniques.
- Microsurgical Anastomosis: The DCIA is meticulously anastomosed to the penile arteries using advanced microsurgical suturing techniques to create a functional arterial bypass, optimizing blood flow to the penis.
- Recovery and Follow-up: Hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to ensure proper healing and recovery following surgery.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Superficial Temporal Artery (STA) PMA
Definition and Details:
Superficial Temporal Artery (STA) PMA utilizes the superficial temporal artery from the scalp as the donor artery for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This procedure may be considered for patients with specific arterial conditions that make the STA suitable for creating a vascular conduit to improve blood flow and erectile function.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Thorough vascular evaluations, including imaging studies and consultations with specialists, to assess arterial suitability and overall health.
- Surgical Procedure: Under general anesthesia, the surgeon harvests the STA from the scalp using microsurgical techniques.
- Arterial Anastomosis: Precise microsurgical techniques are employed to connect the STA to the penile arteries, creating a vascular bypass to enhance blood flow and improve erectile function.
- Post-operative Care: Hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to facilitate healing and prevent complications.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Anterior Tibial Artery (ATA) PMA
Definition and Details:
Anterior Tibial Artery (ATA) PMA involves using the anterior tibial artery, which runs along the front of the leg, as the donor artery for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This procedure is chosen based on the accessibility and vascular characteristics of the ATA, which can provide sufficient blood flow to improve erectile function in patients with specific arterial insufficiencies.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Comprehensive vascular evaluations, including Doppler ultrasound and consultations with specialists, to evaluate arterial anatomy and determine surgical candidacy.
- Surgical Procedure: Under general anesthesia, the surgeon harvests the ATA and prepares it for microsurgical anastomosis.
- Microsurgical Anastomosis: Precise microsurgical techniques are employed to connect the ATA to the penile arteries, creating a vascular bypass to optimize blood flow and erectile function.
- Recovery and Follow-up: Hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to facilitate healing and prevent complications following surgery.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Posterior Tibial Artery (PTA) PMA
Definition and Details:
Posterior Tibial Artery (PTA) PMA utilizes the posterior tibial artery, located in the lower leg, as the donor artery for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This procedure may be considered for patients with specific arterial conditions where the PTA can serve as an effective conduit to enhance blood flow and improve erectile function.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Thorough vascular evaluations, including imaging studies and consultations with specialists, to assess arterial suitability and overall health.
- Surgical Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, the surgeon harvests the PTA and prepares it for microsurgical anastomosis.
- Arterial Anastomosis: Precise microsurgical techniques are utilized to connect the PTA to the penile arteries, creating a vascular bypass to optimize blood flow and erectile function.
- Post-operative Care: Hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to ensure proper healing and recovery following surgery.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Lateral Circumflex Femoral Artery (LCFA) PMA
Definition and Details:
Lateral Circumflex Femoral Artery (LCFA) PMA involves utilizing the lateral circumflex femoral artery, which originates from the femoral artery in the thigh, as the donor artery for microsurgical arterial bypass to the penile arteries.
This procedure is chosen based on the anatomical proximity and vascular characteristics of the LCFA, which can provide sufficient blood flow to enhance erectile function in patients with specific arterial insufficiencies.
Procedure Steps:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Comprehensive vascular evaluations, including Doppler ultrasound and consultations with specialists, to assess arterial anatomy and determine surgical candidacy.
- Surgical Procedure: Under general anesthesia, the surgeon identifies and prepares the LCFA using microsurgical techniques.
- Microsurgical Anastomosis: Precise microsurgical techniques are employed to connect the LCFA to the penile arteries, creating a vascular bypass to optimize blood flow and erectile function.
- Recovery and Follow-up: Hospitalization for monitoring, pain management, and wound care to facilitate healing and prevent complications following surgery.
Pricing Breakdown:
- Surgeon’s Fee: $3,000 – $6,000 USD
- Hospital Fees: $1,000 – $2,000 USD (per day)
- Anesthesia: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Pre-operative Assessments: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Medications and Post-operative Care: $500 – $1,000 USD
- Travel and Accommodation: $50 – $200 USD per night
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,500 – $10,000 USD (excluding travel and accommodation)
Price Comparison of Penile Microsurgical Artery Anastomosis (PMA) Procedures in the major cities in Turkey.
Radial Artery PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $800
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,000
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $800
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $700
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $8,800
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $700
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,500
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,200
- Anesthesia – $700
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $600
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $7,700
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $750
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,800
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,300
- Anesthesia – $750
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $650
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $8,250
Saphenous Vein PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $850
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,200
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,600
- Anesthesia – $850
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $750
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $9,250
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $800
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,800
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,400
- Anesthesia – $800
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $700
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $8,500
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $825
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,000
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $825
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $725
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $9,075
Internal Pudendal Artery PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $800
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,000
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $800
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $700
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $8,800
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $700
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,500
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,200
- Anesthesia – $700
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $600
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $7,700
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $750
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,800
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,300
- Anesthesia – $750
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $650
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $8,250
Deep Circumflex Iliac Artery (DCIA) PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $900
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,300
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,700
- Anesthesia – $900
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $800
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $9,600
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $850
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,900
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $850
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $750
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $8,850
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $875
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,200
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,600
- Anesthesia – $875
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $775
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $9,325
Superficial Temporal Artery (STA) PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $850
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,200
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,600
- Anesthesia – $850
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $750
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $9,250
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $800
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,800
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,400
- Anesthesia – $800
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $700
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $8,500
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $825
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,000
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $825
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $725
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $9,075
Anterior Tibial Artery (ATA) PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $875
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,100
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,650
- Anesthesia – $875
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $775
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $9,275
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $825
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,700
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,450
- Anesthesia – $825
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $725
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $8,425
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $825
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,000
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $825
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $725
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $9,075
Posterior Tibial Artery (PTA) PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $850
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,200
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,600
- Anesthesia – $850
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $750
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $9,250
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $800
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,800
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,400
- Anesthesia – $800
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $700
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $8,500
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $825
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,000
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $825
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $725
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $9,075
Lateral Circumflex Femoral Artery (LCFA) PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $900
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,300
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,700
- Anesthesia – $900
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $800
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $9,600
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $850
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,900
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $850
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $750
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $8,850
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $875
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,200
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,600
- Anesthesia – $875
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $775
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $9,325
- Inferior Epigastric Artery (IEA) PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $850
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,200
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,600
- Anesthesia – $850
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $750
- Follow-up Consultations – $300
- Blood Tests – $150
- Imaging (Ultrasound, MRI) – $500
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $10,200
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $800
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,800
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,400
- Anesthesia – $800
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $700
- Follow-up Consultations – $250
- Blood Tests – $140
- Imaging (Ultrasound, MRI) – $450
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $9,340
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $825
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,000
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $825
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $725
- Follow-up Consultations – $275
- Blood Tests – $145
- Imaging (Ultrasound, MRI) – $475
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $9,770
Superior Gluteal Artery (SGA) PMA
Istanbul:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $900
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,300
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,700
- Anesthesia – $900
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $800
- Follow-up Consultations – $320
- Blood Tests – $160
- Imaging (Ultrasound, MRI) – $520
- Total Estimated Cost in Istanbul: $10,600
Ankara:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $850
- Surgeon’s Fee – $4,900
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,500
- Anesthesia – $850
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $750
- Follow-up Consultations – $270
- Blood Tests – $150
- Imaging (Ultrasound, MRI) – $480
- Total Estimated Cost in Ankara: $9,750
Izmir:
- Pre-operative Assessments – $875
- Surgeon’s Fee – $5,200
- Hospital Fees (per day) – $1,600
- Anesthesia – $875
- Medications and Post-operative Care – $775
- Follow-up Consultations – $290
- Blood Tests – $155
- Imaging (Ultrasound, MRI) – $500
- Total Estimated Cost in Izmir: $10,270
Factors Influencing the Price Differences of PMA Procedures between Istanbul, Ankara, and Izmir
Medical Infrastructure and Facilities
Istanbul:
- High-End Facilities: Istanbul is home to some of the most advanced and well-equipped medical facilities in Turkey. Many hospitals are accredited by international bodies such as the Joint Commission International (JCI), ensuring high standards of care. These facilities often feature state-of-the-art equipment, advanced diagnostic tools, and luxurious patient rooms, which can drive up costs.
- Research and Development: Being a major medical hub, Istanbul sees significant investments in research and development. Hospitals frequently engage in clinical trials and innovative treatment protocols, attracting top-tier medical professionals. This focus on cutting-edge treatments and technologies, however, contributes to higher operational costs.
- High Operational Costs: The operational costs in Istanbul, including utilities, technology maintenance, and administrative expenses, are generally higher due to the city’s metropolitan nature. The high cost of living and real estate prices also contribute to the increased expenses of running medical facilities.
Ankara:
- Government Hospitals: As the capital city, Ankara has numerous government hospitals that offer medical services at subsidized rates. These hospitals benefit from government funding and support, which can significantly lower the overall cost of procedures.
- Balanced Infrastructure: While Ankara has good medical facilities, the costs are often balanced by governmental support and lower operational costs compared to Istanbul. The city’s medical infrastructure is designed to serve a broad population, providing high-quality care without the premium pricing seen in more commercial medical hubs.
- Less Competition: With fewer private hospitals compared to Istanbul, the medical market in Ankara is less competitive. This often results in more regulated pricing, ensuring that healthcare remains accessible to a wider population.
Izmir:
- Growing Medical Hub: Izmir is developing as a medical destination but is not yet on par with Istanbul or Ankara. The facilities are generally good but often not as advanced or luxurious, leading to more moderate pricing.
- Regional Hospitals: Many regional hospitals in Izmir provide quality care but at lower costs due to reduced operational expenses and regional economic factors. These hospitals might not have the latest technology but offer competent and effective medical treatments.
- Emerging Market: As an emerging market for medical tourism, Izmir hospitals may offer competitive pricing to attract more patients. The city is gradually investing in better infrastructure and facilities to boost its reputation as a medical destination.
Surgeon Expertise and Reputation
Istanbul:
- Top Surgeons: Istanbul attracts some of the most renowned surgeons in Turkey and internationally. These highly experienced and specialized surgeons often command higher fees due to their expertise, training, and the successful outcomes they are known for.
- High Demand: The high demand for skilled surgeons in a competitive market like Istanbul leads to higher fees. Patients are willing to pay a premium for the assurance of being treated by top-tier medical professionals.
- International Recognition: Many surgeons in Istanbul have international recognition and affiliations, which adds to their prestige and the cost of their services. This is particularly appealing to medical tourists seeking world-class treatment.
Ankara:
- Government Employed Surgeons: Many skilled surgeons in Ankara are employed by government hospitals where the cost is subsidized, making procedures more affordable for patients. These surgeons often have extensive experience and training, providing high-quality care at lower prices.
- Academic Surgeons: Being an academic hub, many surgeons in Ankara are also educators and researchers. They work in teaching hospitals where the focus is on providing excellent care and training the next generation of doctors. This dual role often allows for lower procedural costs while maintaining high standards of treatment.
Izmir:
- Experienced Surgeons: Izmir has a mix of experienced surgeons, though not as many top-tier international names as Istanbul. This leads to moderately priced services that still offer quality care.
- Attracting Talent: As Izmir grows as a medical hub, more experienced and reputable surgeons are starting to practice there. This influx of talent is gradually increasing the prices but also enhancing the quality of care available.
Geographical and Economic Factors
Istanbul:
- Metropolitan Costs: Being a major metropolitan city, the cost of living, rent, and other expenses are higher in Istanbul. This translates to higher medical procedure costs as hospitals and clinics need to cover these additional expenses.
- Economic Hub: As the economic center of Turkey, the high cost of services and goods also reflects in medical procedure pricing. The bustling economy drives demand for premium services, including healthcare.
Ankara:
- Government Seat: As the administrative center, the cost of services in Ankara is often lower due to government regulation and subsidies. The presence of numerous government institutions ensures that healthcare remains accessible and affordable.
- Economic Stability: The economic stability provided by government institutions and policies helps keep the cost of procedures relatively lower. Ankara’s economy is less driven by commercial forces, allowing for more controlled pricing in the healthcare sector.
Izmir:
- Regional Differences: The cost of living in Izmir is lower than in Istanbul but higher than in some other parts of Turkey, affecting medical procedure pricing. The regional economic factors, including lower real estate and operational costs, contribute to more affordable healthcare.
- Economic Growth: As an economically growing city, prices in Izmir are moderate but expected to rise as the city develops further. The improving economy and infrastructure investments are likely to influence medical costs gradually.
Medical Tourism Influence
Istanbul:
- High Influx of Medical Tourists: Istanbul is a major destination for medical tourists, which increases demand and consequently, prices. The city’s reputation for high-quality medical care attracts patients from all over the world willing to pay a premium.
- Marketing and Package Deals: Many hospitals in Istanbul offer comprehensive packages for international patients, including accommodation, travel, and concierge services. While convenient, these packages can significantly increase overall costs.
Ankara:
- Moderate Medical Tourism: While Ankara attracts medical tourists, the influx is not as high as in Istanbul. This helps keep prices relatively lower, as the demand from international patients is less intense.
- Government Initiatives: Government initiatives to promote medical tourism often come with subsidies and lower prices, making healthcare affordable and attractive for international patients seeking cost-effective options.
Izmir:
- Emerging Medical Tourism: As an emerging destination for medical tourism, Izmir offers competitive pricing to attract international patients. Hospitals are investing in marketing and infrastructure to appeal to this growing market segment.
- Promotional Packages: Similar to Istanbul, Izmir hospitals offer packages to international patients, but often at lower costs. These packages may include travel and accommodation, making them attractive to medical tourists seeking affordable yet quality care.
Operational and Administrative Costs
Istanbul:
- Higher Operational Costs: The cost of running a medical facility in Istanbul, including staff salaries, utilities, and administrative expenses, is higher. The city’s high cost of living and real estate prices contribute to these increased operational costs.
- Complex Administration: Larger hospitals with complex administrative structures often have higher operational costs, which are reflected in the procedure pricing. The need for extensive staff, advanced technology, and comprehensive patient services adds to the overall expenses.
Ankara:
- Subsidized Costs: Many hospitals in Ankara benefit from government subsidies, which help reduce operational and administrative costs. These subsidies make healthcare more affordable for patients.
- Efficient Administration: Government and teaching hospitals in Ankara often have more efficient administrative systems, keeping costs lower. Streamlined operations and government support ensure that procedures are offered at competitive prices.
Izmir:
- Moderate Operational Costs: The operational costs in Izmir are moderate, contributing to the moderate pricing of medical procedures. The city’s lower cost of living and real estate prices help keep operational expenses manageable.
- Developing Infrastructure: As the medical infrastructure in Izmir develops, operational costs are gradually increasing but still remain lower than in Istanbul. Investments in better facilities and equipment are driving up costs slowly.
Cost of Medical Equipment and Supplies
Istanbul:
- High-End Equipment: Hospitals in Istanbul often use the latest medical equipment and supplies, which are expensive and add to the overall cost of procedures. Advanced diagnostic tools, surgical instruments, and post-operative care technologies contribute to higher prices.
- Frequent Upgrades: Frequent upgrades to maintain cutting-edge technology also drive up costs. Hospitals strive to stay ahead in the competitive market by offering the best possible care, which requires significant investments.
Ankara:
- Standard Equipment: Hospitals in Ankara use high-quality but not necessarily the latest equipment, keeping costs balanced. The focus is on providing effective care with reliable technology that does not require frequent expensive upgrades.
- Government Supply Chains: Government support in procuring medical supplies at lower costs helps reduce procedure prices. Bulk purchasing and state-negotiated rates for supplies ensure that hospitals can offer affordable care.
Izmir:
- Moderate Equipment Costs: The cost of medical equipment in Izmir is moderate, reflecting the overall moderate pricing of procedures. Hospitals may not have the latest technology but ensure that their equipment is effective and well-maintained.
- Growing Market: As the market grows, investments in better equipment are increasing, gradually influencing prices. Hospitals are upgrading their facilities to attract more patients, which is expected to drive costs higher over time.
Patient Services and Care Quality
Istanbul:
- Premium Services: Many hospitals in Istanbul offer premium patient services, including private rooms, concierge services, and personalized care plans. These additional services enhance patient comfort and satisfaction but come at a higher cost.
- Comprehensive Care: The comprehensive care offered, from pre-operative consultations to post-operative follow-ups, is designed to ensure the best outcomes but also adds to the overall cost.
Ankara:
- Standard Services: Patient services in Ankara are typically high-quality but more standard compared to the premium offerings in Istanbul. Government hospitals focus on providing essential care efficiently and affordably.
- Integrated Care: The integration of care in teaching hospitals ensures that patients receive comprehensive treatment without the added costs of luxury services. The focus is on medical effectiveness and patient well-being.
Izmir:
- Growing Patient Services: As Izmir develops as a medical hub, hospitals are starting to offer better patient services. The level of care is improving, but costs remain moderate due to the city’s developing market.
- Competitive Offerings: Hospitals in Izmir offer competitive patient services to attract more patients, providing good care at reasonable prices. The focus is on balancing quality and affordability to build a reputation as a reliable medical destination.
Additional Costs to Consider
Post-operative Care and Medications
After the PMA procedure, patients require post-operative care, including medications to manage pain, prevent infection, and aid recovery.
The cost of medications and follow-up consultations can amount to $500 to $1,000 USD.
Travel and Accommodation
For international patients traveling to Turkey for PMA surgery, travel expenses such as flights and accommodation must be considered. Accommodation costs in Turkey vary widely depending on the city and type of lodging chosen, ranging from $50 to $200 USD per night.
Currency Exchange and Payment Methods
Understanding currency exchange rates and payment methods is essential for international patients. Many Turkish clinics accept various currencies and payment methods, including credit cards and bank transfers.
It’s advisable to clarify payment terms and any potential additional charges beforehand.
Insurance and Financing Options
Medical Insurance Coverage
While elective procedures like PMA may not be covered by insurance, it’s crucial to check with both your domestic insurer and potential Turkish healthcare providers.
Some international insurers may offer partial coverage or reimbursement for medically necessary procedures.
Financing and Payment Plans
Many Turkish clinics offer financing options or payment plans to assist patients in managing upfront costs.
These plans may include installment payments or financing through medical loan providers. Patients should inquire about these options during the initial consultation.
Preparations Before Undergoing PMA Procedure: Personal and Doctor-Directed Steps
Personal Preparations
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Healthy Diet: Prior to surgery, maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins is crucial. Nutrients such as Vitamin C, Zinc, and proteins aid in tissue repair and recovery. Avoid processed foods and focus on fresh fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains.
- Hydration: Proper hydration is vital for overall health and aids in recovery. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day. Avoid caffeinated and sugary beverages as they can lead to dehydration.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps improve circulation and overall fitness, which can contribute to a smoother recovery. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling are recommended. Avoid strenuous activities that could cause injury.
Smoking and Alcohol
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can significantly impair healing and increase the risk of complications. It’s advised to quit smoking at least 4-6 weeks before the procedure to enhance recovery and outcomes.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with medications and affect your body’s ability to heal. Reduce alcohol intake or avoid it altogether in the weeks leading up to the surgery.
Medications and Supplements
- Medication Review: Inform your doctor about all the medications you are currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and supplements. Some medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be discontinued before surgery.
- Supplements: Certain supplements, such as Vitamin E, fish oils, and herbal supplements, can increase bleeding risk. Consult with your doctor about which supplements to avoid.
Mental and Emotional Preparation
- Stress Management: Undergoing surgery can be stressful. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to maintain mental well-being.
- Support System: Ensure you have a reliable support system in place. Discuss your surgery with family or friends and arrange for someone to accompany you on the day of the procedure and assist during the initial recovery period.
Personal Hygiene
- Pre-Surgical Bathing: Follow any specific bathing instructions provided by your surgeon. This may include using antiseptic soap to reduce the risk of infection.
- Shaving Instructions: Your doctor may advise on whether you need to shave the surgical area. Avoid shaving on your own unless instructed, as improper shaving can cause skin irritation or infection.
Clothing and Comfort
- Comfortable Clothing: On the day of the surgery, wear loose, comfortable clothing that is easy to remove and put back on. Consider button-up shirts and drawstring pants.
- Personal Items: Prepare a small bag with personal items you might need at the hospital, such as a phone charger, reading materials, and any necessary medications.
Preparations with the Doctor
Initial Consultation
- Medical History: During your initial consultation, provide your doctor with a comprehensive medical history, including any previous surgeries, chronic conditions, allergies, and current medications.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination will be conducted to assess your overall health and suitability for the procedure. This may include blood tests, urine tests, and cardiovascular assessments.
Pre-Surgical Testing
- Diagnostic Tests: Your doctor may order specific diagnostic tests to evaluate the condition of your penile arteries. These could include Doppler ultrasound, angiography, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Blood Tests: Routine blood tests will be conducted to check for any underlying health issues, such as anemia or infection, that could affect surgery or recovery.
Pre-Surgical Instructions
- Fasting Guidelines: Your doctor will provide fasting instructions, typically requiring you to avoid eating or drinking for 8-12 hours before the surgery. This helps prevent complications related to anesthesia.
- Medication Adjustments: Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding any adjustments to your medication regimen. This may include temporarily stopping blood thinners, anti-inflammatory drugs, or certain supplements.
Anesthesia Consultation
- Anesthesiologist Meeting: You will have a consultation with the anesthesiologist to discuss your medical history, any previous experiences with anesthesia, and the type of anesthesia to be used during the procedure.
- Allergy Assessment: Inform the anesthesiologist about any known allergies, especially to medications or anesthesia agents, to prevent adverse reactions.
Informed Consent
- Procedure Explanation: Your doctor will provide a detailed explanation of the PMA procedure, including the steps involved, potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes.
- Consent Form: You will be required to sign an informed consent form, indicating that you understand the procedure and agree to proceed. Ensure all your questions and concerns are addressed before signing.
Pre-Operative Planning
- Surgical Plan: The surgeon will outline the surgical plan, including the specific technique to be used, the expected duration of the procedure, and the anticipated recovery process.
- Post-Operative Care: Discuss the post-operative care plan, including wound care, pain management, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
Financial Arrangements
- Cost Estimate: Obtain a detailed cost estimate from your healthcare provider, including the surgeon’s fee, hospital charges, anesthesia costs, and any additional expenses.
- Insurance Coverage: Verify your insurance coverage and understand what costs will be covered and what out-of-pocket expenses you may incur. Discuss payment plans or financing options if needed.
Day of Surgery
- Arrival Time: Arrive at the hospital or surgical center at the designated time, allowing for sufficient time to complete any last-minute paperwork or pre-operative preparations.
- Identification and Paperwork: Bring a form of identification and any necessary paperwork, including insurance cards and consent forms.
Pre-Operative Preparations
- Vital Signs Monitoring: Upon arrival, your vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, temperature) will be monitored to ensure you are in optimal condition for surgery.
- Intravenous Line: An intravenous (IV) line will be inserted to administer fluids, medications, and anesthesia during the procedure.
Final Consultation
- Surgeon Meeting: You will have a final consultation with your surgeon to review the procedure and address any last-minute questions or concerns.
- Anesthesia Administration: The anesthesiologist will administer anesthesia, and you will be closely monitored until the procedure begins.
Post-Operative Care Instructions
- Wound Care: Your surgeon will provide detailed instructions on how to care for the surgical site, including how to change dressings and recognize signs of infection.
- Activity Restrictions: Follow your doctor’s guidelines regarding physical activity, including lifting restrictions, exercise limitations, and sexual activity.
- Pain Management: Your doctor will prescribe pain medications to manage post-operative discomfort. Follow the dosage instructions carefully and report any side effects.
Follow-Up Appointments
- Scheduled Visits: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and address any complications or concerns. These visits are crucial for ensuring a successful recovery.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Your doctor may recommend ongoing monitoring of your condition, including regular check-ups and diagnostic tests, to assess the long-term success of the procedure.
Detailed Steps of the Penile Microsurgical Artery Anastomosis (PMA) Procedure
Anesthesia Administration
Pre-Operative Anesthesia Preparation:
- Patient Positioning: The patient is positioned on the operating table, typically in a supine position. This ensures optimal access to the surgical site and allows for efficient monitoring of the patient’s vital signs.
- Monitoring Devices: Various monitoring devices are connected to the patient to continuously track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and respiratory rate throughout the procedure. This ensures any abnormalities are immediately detected and managed.
Administration of Anesthesia:
- General Anesthesia: Most PMA procedures are performed under general anesthesia. This involves putting the patient into a deep sleep, ensuring they are pain-free and unconscious during the surgery.
- Anesthesia Induction: Intravenous (IV) medications are administered to induce anesthesia. These include anesthetic agents that induce unconsciousness, muscle relaxants to prevent involuntary movements, and analgesics to manage pain.
- Airway Management: A breathing tube is inserted into the patient’s windpipe (trachea) to maintain an open airway and facilitate mechanical ventilation during the procedure. This ensures the patient receives adequate oxygen throughout the surgery.
Surgical Site Preparation
Sterilization and Draping:
- Skin Disinfection: The surgical area, including the lower abdomen and genital region, is thoroughly cleaned with antiseptic solutions. This step is crucial to minimize the risk of infection and ensure a sterile environment.
- Sterile Draping: Sterile drapes are placed around the surgical site to create a sterile field. This isolates the operative area from potential contaminants, maintaining the sterility of the procedure.
Incision and Exposure
Initial Incision:
- Inguinal Incision: A small incision is made in the groin area (inguinal region) to access the femoral artery, which serves as the donor artery for the anastomosis. This incision is typically about 2-3 cm in length.
- Penile Incision: Another small incision is made along the shaft of the penis to expose the recipient penile arteries, typically the dorsal penile arteries. This incision is made with precision to avoid damage to surrounding tissues.
Exposure of Arteries:
- Dissection: Careful dissection is performed to expose the femoral artery in the groin and the dorsal penile arteries in the penis. This involves separating the arteries from surrounding tissues and structures while preserving the integrity of nearby nerves and veins.
- Use of Retractors: Surgical retractors are used to hold back surrounding tissues and provide a clear view of the arteries. This facilitates accurate and precise dissection and preparation of the arteries for anastomosis.
Harvesting the Donor Artery
Identification of Donor Artery:
- Femoral Artery: The femoral artery, located in the groin, is identified as the donor artery. It is chosen for its size, accessibility, and suitability for microsurgical anastomosis. The artery is carefully assessed to ensure it is free from disease or damage.
Artery Mobilization:
- Dissection: The femoral artery is carefully dissected free from surrounding tissues, ensuring adequate length and mobility for the anastomosis. The artery is handled gently to avoid trauma and ensure its viability.
- Temporary Clamping: Temporary microvascular clamps are placed on the femoral artery to control blood flow during the anastomosis procedure. These clamps are applied with minimal pressure to avoid damaging the artery.
Preparing the Recipient Artery
Identification of Recipient Arteries:
- Dorsal Penile Arteries: The dorsal penile arteries, located along the shaft of the penis, are identified as the recipient arteries. These arteries are responsible for supplying blood to the penile tissue and are carefully evaluated to ensure they are suitable for anastomosis.
Artery Preparation:
- Dissection: The dorsal penile arteries are carefully dissected free from surrounding tissues, ensuring clear access for the anastomosis. The dissection is performed with precision to preserve the integrity of the arteries and surrounding structures.
- Temporary Clamping: Temporary microvascular clamps are placed on the dorsal penile arteries to control blood flow and facilitate precise anastomosis. The clamps are applied gently to avoid damaging the arteries.
Microsurgical Anastomosis
Microsurgical Technique:
- Microscope Setup: A high-powered surgical microscope is positioned over the surgical field to provide magnification and enhanced visualization of the tiny blood vessels. The microscope is adjusted to ensure optimal clarity and detail.
- Microsurgical Instruments: Specialized microsurgical instruments, including fine needles, sutures, and forceps, are used to perform the delicate anastomosis. These instruments are designed to handle the small and delicate structures involved in the procedure.
Anastomosis Procedure:
- Arteriotomy: Small incisions (arteriotomies) are made in both the donor (femoral) and recipient (dorsal penile) arteries to create openings for the anastomosis. These incisions are made with precision to ensure they are of the correct size and shape.
- End-to-End Anastomosis: The ends of the femoral artery and dorsal penile arteries are carefully aligned and sutured together using extremely fine, non-reactive sutures (typically 10-0 or 11-0 nylon). The sutures are placed meticulously to ensure a watertight and tension-free connection. The alignment of the arteries is checked repeatedly to ensure the anastomosis is accurate.
- Patency Check: Once the anastomosis is complete, the temporary clamps are gradually released, and blood flow is restored to the penile arteries. The patency of the anastomosis is checked using Doppler ultrasound or other imaging techniques to ensure proper blood flow. This step is crucial to confirm the success of the procedure.
Hemostasis and Wound Closure
Hemostasis:
- Bleeding Control: Any bleeding from the surgical site is meticulously controlled using electrocautery, sutures, or hemostatic agents. This ensures the surgical field remains clear and reduces the risk of post-operative bleeding.
- Hemostatic Agents: Hemostatic agents, such as collagen sponges or fibrin sealants, may be applied to enhance clot formation and reduce bleeding. These agents are used sparingly to avoid interfering with the healing process.
Wound Closure:
- Layered Closure: The incisions in the groin and penis are closed in layers using absorbable sutures for deeper tissues and non-absorbable sutures or skin adhesives for the skin. This technique ensures a secure and cosmetically acceptable closure.
- Dressing Application: Sterile dressings are applied to the incision sites to protect the wounds and promote healing. The dressings are chosen to provide optimal coverage and support.
Immediate Post-Operative Monitoring
Monitoring and Recovery:
- Transfer to Recovery Room: The patient is transferred to the recovery room, where they are closely monitored as they awaken from anesthesia. This ensures any immediate post-operative issues are promptly addressed.
- Vital Sign Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation, is conducted to ensure patient stability. Any deviations from normal values are investigated and managed.
Pain Management:
- Post-Operative Pain: Post-operative pain is managed using prescribed analgesics. The patient’s pain levels are regularly assessed and addressed to ensure comfort and promote recovery.
- Patient Education: The patient is educated on pain management techniques, including the use of medications and non-pharmacological methods such as ice packs and elevation.
Initial Assessment:
- Vascular Patency: The patency of the anastomosis is reassessed using Doppler ultrasound or other imaging techniques to confirm adequate blood flow to the penile tissue. This step is crucial to ensure the success of the procedure.
- Wound Inspection: The surgical incisions are inspected for signs of bleeding, infection, or other complications. The wounds are cleaned and dressed as needed to promote healing.
Final Considerations
Documentation and Communication:
- Surgical Report: A detailed surgical report is prepared, documenting the procedure, findings, and any intraoperative complications. This report is included in the patient’s medical records.
- Post-Operative Instructions: The patient is provided with detailed post-operative instructions, including wound care, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments. These instructions are designed to promote recovery and prevent complications.
Follow-Up Care:
- Scheduled Appointments: Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the patient’s progress and address any concerns. These appointments typically occur at regular intervals during the first few weeks after surgery.
- Ongoing Monitoring: The patient’s recovery is monitored closely, with a focus on wound healing, pain management, and the patency of the anastomosis. Any issues that arise are promptly addressed.
Post-Operative Period of Penile Microsurgical Artery Anastomosis (PMA)
Short-Term Healing Period
Immediate Post-Operative Care:
Recovery Room Monitoring:
- Vital Signs Monitoring: After the procedure, patients are transferred to the recovery room, where vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation, are continuously monitored.
- Pain Management: Pain levels are assessed regularly. Patients receive analgesics to manage post-operative discomfort, ensuring a smooth recovery.
Initial Assessment:
- Vascular Patency Check: The patency of the anastomosis is reassessed using Doppler ultrasound or other imaging techniques to confirm adequate blood flow to the penile tissue.
- Wound Inspection: Surgical incisions are inspected for signs of bleeding, infection, or other complications. Wounds are cleaned and redressed as necessary.
Patient Education:
- Post-Operative Instructions: Detailed instructions are provided on wound care, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments. This includes guidelines on how to change dressings, signs of infection to watch for, and activities to avoid to prevent strain on the surgical site.
- Pain Management Techniques: Patients are educated on various pain management techniques, including the proper use of medications and non-pharmacological methods such as ice packs and elevation.
Hospital Stay and Discharge:
Hospital Stay:
- Duration: The typical hospital stay following PMA is 1-2 days, depending on the patient’s overall health and the complexity of the procedure.
- Continued Monitoring: Throughout the hospital stay, continuous monitoring of vital signs and the surgical site is maintained to promptly address any complications.
Discharge Criteria:
- Stability: Patients must be hemodynamically stable with controlled pain and no signs of infection or other complications.
- Ability to Follow Instructions: Patients or their caregivers must demonstrate an understanding of post-operative care instructions, including medication schedules and wound care.
At-Home Care:
Wound Care:
- Dressings: Dressings should be kept clean and dry. Instructions on how to change dressings are provided, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a sterile environment.
- Signs of Infection: Patients are advised to monitor for signs of infection, including redness, swelling, increased pain, or discharge from the wound. Immediate medical attention is required if these signs are observed.
Activity Restrictions:
- Physical Activity: Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sexual activity for several weeks to allow for proper healing.
- Rest and Elevation: Resting and elevating the surgical site can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
Follow-Up Appointments:
- Scheduled Visits: Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the healing process, check the patency of the anastomosis, and address any concerns.
- Assessment: During these visits, the surgical site is inspected, and any necessary adjustments to the post-operative care plan are made.
Long-Term Healing Period
Continued Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Gradual Return to Normal Activities:
- Resuming Activities: Patients can gradually resume normal activities as healing progresses. Physical activities should be reintroduced slowly, with careful monitoring for any signs of discomfort or complications.
- Sexual Activity: Sexual activity can typically be resumed 4-6 weeks post-surgery, but this may vary based on individual healing rates and the surgeon’s advice.
Long-Term Monitoring:
- Regular Check-Ups: Continued follow-up appointments are crucial to ensure long-term success of the procedure. These appointments typically occur at 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter.
- Assessment of Blood Flow: Doppler ultrasound or other imaging techniques may be used periodically to assess the patency of the anastomosis and ensure adequate blood flow to the penile tissue.
Lifestyle and Health Considerations:
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, can significantly impact the long-term success of the PMA procedure.
- Weight Management: Managing weight is essential, as obesity can negatively affect vascular health and the outcome of the surgery.
Management of Underlying Conditions:
- Chronic Conditions: Patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease must manage these conditions effectively to ensure optimal surgical outcomes.
- Medication Adherence: Adhering to prescribed medications, including those for underlying conditions and post-operative care, is crucial for long-term health.
Potential Complications and Their Management:
Short-Term Complications:
- Infection: Infections are a common post-operative risk. Early signs of infection include redness, swelling, increased pain, and discharge. Prompt medical intervention is necessary to manage infections effectively.
- Bleeding: Post-operative bleeding can occur and may require additional medical intervention. Keeping the surgical site clean and following activity restrictions can help minimize this risk.
Long-Term Complications:
- Anastomosis Failure: In rare cases, the anastomosis may fail, leading to inadequate blood flow. Regular monitoring and imaging can help detect and address this issue early.
- Scar Tissue Formation: Scar tissue can form at the surgical site, potentially impacting blood flow. Physical therapy and, in some cases, additional surgical intervention may be required to manage this complication.
Patient Support and Resources:
Support Networks:
- Patient Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide patients with emotional support, information, and shared experiences from others who have undergone similar procedures.
- Family and Friends: Encouragement and assistance from family and friends can significantly enhance the recovery process.
Educational Resources:
- Educational Materials: Access to educational materials, including brochures, videos, and online resources, can help patients understand the procedure, recovery process, and long-term care.
- Consultation with Healthcare Providers: Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including urologists and vascular surgeons, ensure patients receive the necessary guidance and care throughout their recovery.
Psychological and Emotional Support:
Counseling and Therapy:
- Mental Health Support: Post-operative recovery can be emotionally challenging. Access to counseling and therapy can help patients manage anxiety, depression, or other emotional responses.
- Sexual Health Counseling: For many patients, sexual health counseling can provide valuable insights and strategies for resuming a healthy sexual life post-surgery.
Stress Management:
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Incorporating stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can positively impact the healing process and overall well-being.
- Support Systems: Leveraging support systems, whether through family, friends, or professional counselors, can provide significant emotional stability and encouragement during recovery.
Essential Considerations for Foreign Patients Undergoing PMA Procedures in Turkey
Researching the Procedure and Medical Facilities
Understanding the PMA Procedure:
- Procedure Details: Gain a thorough understanding of what the PMA procedure entails, including the surgical technique, expected outcomes, potential risks, and recovery process. Read medical literature, watch educational videos, and consult with medical professionals.
- Success Rates: Investigate the success rates of the PMA procedure in Turkey. Look for reputable sources and studies that provide statistical data on patient outcomes, complication rates, and long-term benefits.
Choosing the Right Medical Facility:
- Accreditation and Certification: Ensure the medical facility is accredited by recognized international organizations, such as Joint Commission International (JCI), which guarantees high standards of care and safety.
- Reputation and Reviews: Research the reputation of the hospital or clinic. Read reviews from previous patients, check online forums, and seek recommendations from trusted sources.
- Specialization and Experience: Choose a facility that specializes in urological and microsurgical procedures. Verify the experience and expertise of the medical team in performing PMA surgeries.
Selecting a Qualified Surgeon
Surgeon’s Credentials:
- Board Certification: Ensure the surgeon is board-certified in urology or a related field. Board certification indicates that the surgeon has met rigorous standards and has the necessary training and expertise.
- Experience and Track Record: Look for a surgeon with extensive experience in performing PMA procedures. Ask about their track record, including the number of surgeries performed and success rates.
- Professional Memberships: Check if the surgeon is a member of reputable professional organizations, such as the European Association of Urology (EAU) or the International Society of Urology (ISU), which reflects their commitment to staying updated with the latest advancements.
Consultation and Communication:
- Initial Consultation: Schedule an initial consultation with the surgeon to discuss your case in detail. This is an opportunity to assess their communication skills, understanding of your needs, and ability to address your concerns.
- Language Barriers: Consider language barriers and ensure effective communication. Choose a surgeon who speaks your language fluently or arrange for a professional medical interpreter to facilitate clear communication.
Financial Considerations
Cost of the Procedure:
- Detailed Cost Estimate: Obtain a detailed cost estimate from the medical facility, including surgeon’s fees, hospital charges, anesthesia costs, pre-operative tests, and post-operative care. Make sure there are no hidden costs.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare the cost of the PMA procedure in Turkey with other countries. Turkey is known for offering high-quality medical services at competitive prices, but ensure you are getting value for your money.
Insurance Coverage:
- Insurance Policies: Review your health insurance policy to determine if the PMA procedure is covered. Some insurance companies may cover part or all of the costs, especially if the surgery is deemed medically necessary.
- Travel Insurance: Consider purchasing travel insurance that covers medical expenses, trip cancellations, and unexpected complications. This provides financial protection in case of unforeseen circumstances.
Payment Options:
- Payment Plans: Inquire about available payment plans or financing options. Many hospitals and clinics in Turkey offer flexible payment plans to accommodate international patients.
- Currency Exchange: Understand the currency exchange rates and payment methods accepted by the medical facility. Some facilities may offer discounts for payments made in cash or specific currencies.
Travel and Accommodation Arrangements
Travel Logistics:
- Flight Arrangements: Book your flights well in advance. Consider the duration of your stay, including time for pre-operative consultations, the procedure, and post-operative recovery.
- Visa Requirements: Check the visa requirements for entering Turkey. Some countries are eligible for e-visas, while others may require a visit to the Turkish consulate.
Accommodation:
- Proximity to Medical Facility: Choose accommodation close to the hospital or clinic to minimize travel time and stress. Many medical facilities offer partnerships with nearby hotels that provide discounted rates for patients.
- Comfort and Amenities: Ensure the accommodation is comfortable and has necessary amenities for a smooth recovery, such as a quiet environment, room service, and accessible facilities.
Transportation:
- Airport Transfers: Arrange for airport transfers to and from your accommodation. Some medical facilities offer complimentary airport pick-up and drop-off services.
- Local Transportation: Plan for local transportation during your stay. This includes trips to the medical facility for pre-operative tests, the surgery, and follow-up appointments.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Medical Regulations:
- Legal Compliance: Ensure the medical facility complies with Turkish medical regulations and ethical standards. This includes adherence to patient safety protocols, sterilization procedures, and ethical practices.
- Informed Consent: Understand the informed consent process. You should receive comprehensive information about the procedure, potential risks, and alternatives before signing any consent forms.
Patient Rights:
- Patient Rights Charter: Familiarize yourself with the patient rights charter in Turkey, which outlines your rights as a patient, including the right to receive information, privacy, and quality care.
- Complaint Mechanisms: Know the mechanisms for lodging complaints if you are dissatisfied with the care received. This includes contacting the hospital administration, professional medical bodies, or legal authorities.
Health and Safety Precautions
Pre-Existing Health Conditions:
- Medical History: Provide a detailed medical history to your surgeon, including any pre-existing conditions, allergies, and previous surgeries. This helps the medical team plan the procedure and manage any potential complications.
- Pre-Operative Tests: Undergo all necessary pre-operative tests, such as blood tests, ECG, and imaging studies, to ensure you are in optimal health for the surgery.
Infection Control:
- Hospital Hygiene: Verify the hospital’s infection control protocols. High standards of cleanliness and sterilization are crucial to prevent post-operative infections.
- Post-Operative Care: Follow all post-operative care instructions meticulously, including wound care, medication adherence, and follow-up appointments, to minimize the risk of complications.
COVID-19 Precautions:
- Travel Restrictions: Stay updated on COVID-19 travel restrictions and guidelines. Ensure you comply with testing and quarantine requirements, if applicable.
- Vaccination Status: Check if the medical facility has specific requirements regarding COVID-19 vaccination status for patients undergoing elective surgeries.
Cultural and Language Considerations
Cultural Sensitivity:
- Respect for Local Customs: Familiarize yourself with Turkish culture and customs. This includes understanding local etiquette, dress codes, and social norms to ensure a respectful and positive experience.
- Dietary Preferences: If you have specific dietary preferences or restrictions, communicate these to the medical facility and your accommodation to ensure your needs are met.
Language Barriers:
- Interpreter Services: Arrange for professional interpreter services if needed. Effective communication is vital for understanding medical instructions and expressing your concerns.
- Bilingual Staff: Choose a medical facility with bilingual staff who can assist you throughout your treatment journey.
Choosing the Right Clinic and Surgeon
Research and Accreditation
When selecting a clinic and surgeon for PMA surgery in Turkey, thorough research is essential.
Look for clinics accredited by reputable international healthcare organizations and surgeons with specialized training in urology and microsurgery.
Patient Reviews and Testimonials
Reading patient reviews and testimonials can provide valuable insights into the quality of care and outcomes at different clinics.
Websites, forums, and social media platforms often feature patient experiences that can help guide your decision-making process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cost of Penile Microsurgical Artery Anastomosis (PMA) procedure in Turkey varies based on several factors, including location, surgeon’s expertise, pre-operative assessments, and post-operative care.
By understanding these pricing factors and considerations, patients can make informed decisions and plan their treatment with confidence.
Turkey’s combination of advanced medical facilities and competitive pricing makes it a popular choice for patients seeking quality healthcare abroad.

