Free online quote
Gastric band surgery, a popular option for weight loss, varies significantly in cost depending on the country and healthcare system.
This comprehensive guide explores the cost comparison between undergoing a gastric band procedure in Dubai versus Turkey. We delve into every aspect of pricing to help potential patients make informed decisions.

What is Gastric Banding?
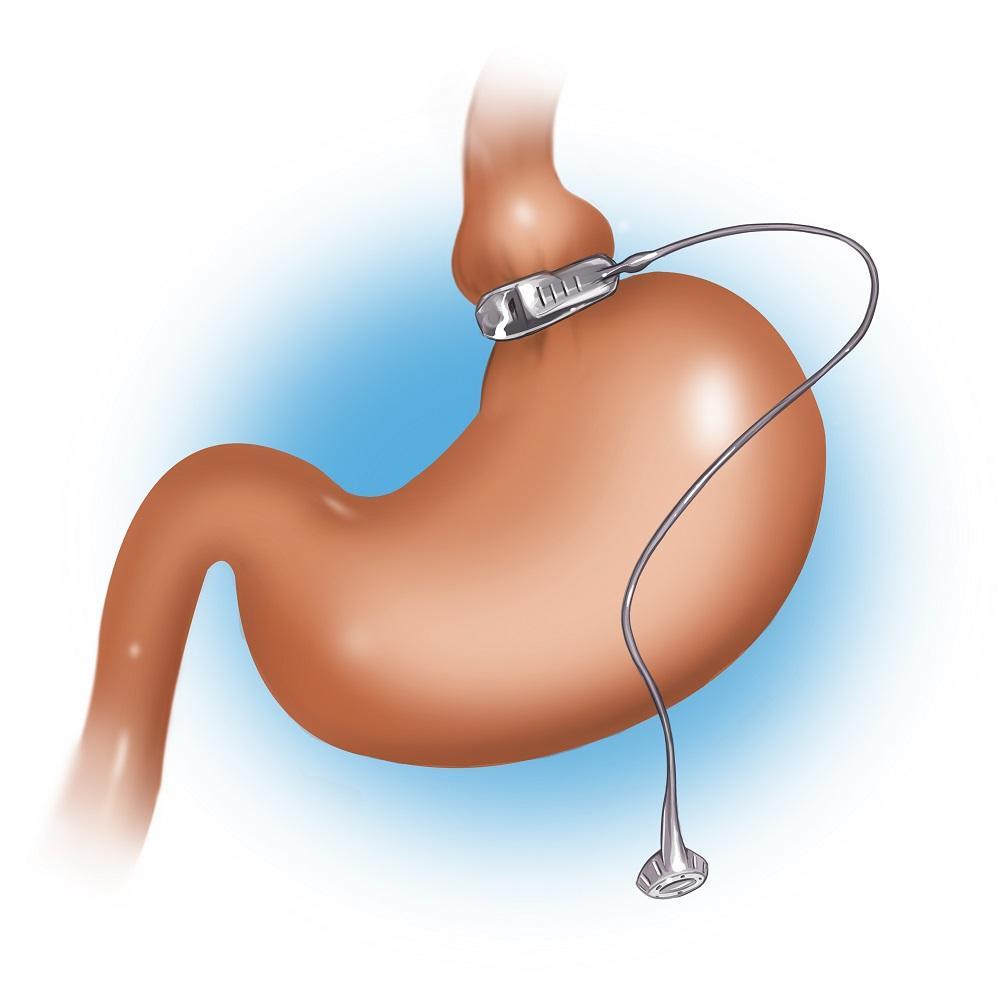
Gastric banding, or laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), is a surgical procedure that involves placing an adjustable silicone band around the upper part of the stomach. This creates a smaller stomach pouch, limiting the amount of food intake and promoting weight loss.
Benefits of Gastric Band Surgery
- Effective Weight Loss: Helps patients achieve significant and sustained weight loss.
- Reversibility: The procedure is reversible and adjustable.
- Low Risk: Generally considered safer compared to other bariatric surgeries like gastric bypass.
Types of the gastric band procedure.
Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)
Definition:
Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to aid weight loss by placing an adjustable silicone band around the upper part of the stomach.
This band creates a small pouch that limits food intake, promoting early satiety and reduced calorie consumption.
LAGB is reversible and adjustable, allowing for modifications in band tightness without additional surgery.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Includes comprehensive medical history review, physical examination, and various tests (e.g., blood work, imaging) to assess the patient’s overall health and suitability for surgery.
- Surgical Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, LAGB involves making several small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon places the adjustable silicone band around the upper stomach to create a small pouch, which is secured in place.
- Placement of Access Port: A small access port is typically secured beneath the skin of the abdomen and connected to the silicone band via tubing. This access port allows for adjustments to the band’s tightness post-operatively.
- Adjustment Phase: Post-surgery, adjustments to the band are made by injecting or withdrawing saline through the access port. This allows for customization of the band’s tightness based on the patient’s weight loss progress and individual needs.
Benefits:
- Reversibility: LAGB is considered reversible, as the band can be removed if necessary, restoring the stomach to its original size.
- Adjustability: One of the primary advantages of LAGB is its adjustability. The degree of restriction can be modified over time without additional surgery, making it a versatile option for patients.
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to more invasive procedures like gastric bypass, LAGB typically results in shorter hospital stays, reduced recovery time, and fewer complications.
- Lower Risk of Nutritional Deficiencies: Since LAGB does not involve altering the digestive tract or rerouting of the intestines, the risk of malabsorption and nutritional deficiencies is lower.
Considerations:
- Slower Weight Loss: Weight loss with LAGB may be gradual compared to other bariatric surgeries, requiring patience and adherence to post-operative guidelines.
- Potential for Complications: While generally safe, complications such as band slippage, erosion, or leakage may occur, necessitating further medical intervention.
- Regular Monitoring Required: Successful outcomes with LAGB require regular follow-up visits to adjust the band’s tightness and monitor for potential complications.
- Patient Compliance: Long-term success hinges on patient compliance with dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and follow-up care to achieve and maintain weight loss goals.
Adjustable Gastric Balloon (AGB)
Definition:
Adjustable Gastric Balloon (AGB) is a non-surgical, temporary weight loss procedure that involves placing an inflatable silicone balloon in the stomach to create a feeling of fullness and reduce hunger.
The balloon occupies space in the stomach, limiting food intake and promoting weight loss over a defined period.
AGB is often used as a bridge to more permanent weight loss solutions or to help patients achieve significant weight loss before elective surgeries.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Prior to AGB placement, patients undergo thorough medical assessments, nutritional counseling, and sometimes endoscopic evaluation to ensure the stomach is suitable for balloon placement.
- Balloon Placement Procedure: AGB insertion is performed under light sedation or general anesthesia. An endoscope is used to guide the deflated silicone balloon into the stomach through the mouth.
- Inflation of the Balloon: Once properly positioned within the stomach, the balloon is filled with a sterile saline solution or gas (e.g., air) to expand and occupy space.
- Monitoring and Post-procedure Care: Patients are monitored closely following balloon placement to manage potential side effects such as nausea, discomfort, or vomiting during the initial adjustment phase.
Benefits:
- Non-surgical: AGB does not involve incisions or alterations to the digestive anatomy, resulting in reduced recovery time and minimized risk of surgical complications.
- Temporary Weight Loss Aid: The balloon is typically left in place for 6-12 months to facilitate significant weight loss and encourage adoption of healthier eating habits.
- Early Satiety: By occupying space in the stomach, the balloon promotes early feelings of fullness, helping patients consume smaller portions and reduce overall calorie intake.
- Bridge to Long-term Solutions: AGB can serve as a temporary measure to initiate weight loss and improve health outcomes before considering more permanent bariatric procedures.
Considerations:
- Temporary Nature: Weight loss achieved with AGB is temporary, and sustained results depend on continued adherence to diet and lifestyle changes.
- Side Effects and Adjustments: Initial discomfort, nausea, or vomiting may occur as the body adjusts to the presence of the balloon. Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor and adjust as needed.
- Patient Selection: AGB may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain gastrointestinal conditions or extensive obesity where more permanent solutions may be required.
- Supportive Care: Success with AGB hinges on comprehensive support, including nutritional counseling, behavioral therapy, and ongoing medical supervision to optimize weight loss outcomes.
Gastric Band Revision Surgery
Definition:
Gastric Band Revision Surgery refers to additional procedures performed on patients who have previously undergone gastric banding but require adjustments, replacements, or corrections due to complications, inadequate weight loss, or changes in health status.
These revisions may involve band removal, replacement, conversion to another bariatric procedure, or addressing complications such as band slippage, erosion, or inadequate weight loss.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Patients undergo comprehensive medical assessments, review of prior surgical history, and diagnostic tests to determine the reasons for revision surgery and assess overall health status.
- Revision Procedure: Depending on the specific needs, revisions may involve laparoscopic or open surgical techniques to address complications such as band repositioning, replacement, or conversion to another procedure like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.
- Adjustment and Monitoring: Following revision surgery, patients require close monitoring to manage recovery, assess for complications, and optimize outcomes based on the revised surgical approach.
Benefits:
- Correction of Complications: Provides solutions for complications associated with initial gastric banding, such as band slippage, erosion, or insufficient weight loss.
- Improvement in Weight Loss Outcomes: Revision surgery aims to enhance weight loss results by addressing factors that may have hindered success with the initial procedure.
- Adaptability to Changing Health Needs: Allows for adjustments to accommodate changes in health status, weight loss goals, or lifestyle modifications over time.
- Customization of Treatment: Provides flexibility to tailor surgical interventions based on individual patient needs and circumstances.
Considerations:
- Complexity of Surgery: Revision procedures may be more complex than initial surgeries, requiring expertise in managing prior surgical alterations and potential anatomical changes.
- Risk of Complications: Revision surgeries carry inherent risks such as infection, bleeding, or injury to surrounding tissues due to scar tissue formation from previous operations.
- Patient Expectations: Realistic expectations and commitment to post-operative care are crucial for achieving successful outcomes with revision surgery.
- Long-term Follow-up: Continuous monitoring and follow-up care are essential to monitor for recurrence of complications and ensure sustainable weight loss maintenance.
Mini-Gastric Bypass (MGB)
Definition:
Mini-Gastric Bypass (MGB), also known as Single Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (SAGB), is a simplified form of gastric bypass surgery that involves creating a small stomach pouch and bypassing a portion of the small intestine to reduce the absorption of calories and nutrients.
MGB aims to achieve significant weight loss by restricting food intake and altering digestive processes to promote early satiety and improved metabolic function.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Includes comprehensive medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests (e.g., blood work, imaging) to assess candidacy for surgery and identify potential risk factors.
- Surgical Procedure: Conducted under general anesthesia, MGB begins with the creation of a small stomach pouch using stapling devices or surgical sutures to partition the upper stomach.
- Bypass and Anastomosis: A section of the small intestine is then connected to the newly created stomach pouch, bypassing a portion of the digestive tract to reduce calorie absorption.
- Closure and Recovery: The procedure concludes with closure of incisions and careful monitoring of the patient’s recovery in the hospital or surgical facility.
Benefits:
- Effective Weight Loss: MGB typically results in significant and sustained weight loss comparable to traditional gastric bypass procedures.
- Metabolic Benefits: Improves metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia through weight loss and altered nutrient absorption.
- Reduced Hunger: By altering gut hormones and digestive processes, MGB promotes early satiety and reduces hunger, aiding in adherence to dietary guidelines.
- Potential for Revision: MGB allows for potential adjustments or revisions in the future to optimize weight loss outcomes based on individual patient needs.
Considerations:
- Risk of Complications: Potential risks include anastomotic leaks, internal herniation, and nutritional deficiencies requiring lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation.
- Nutritional Monitoring: Regular monitoring and supplementation of essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and folate are essential to prevent deficiencies post-MGB.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Long-term success with MGB requires adherence to dietary recommendations, regular physical activity, and ongoing medical supervision to maintain weight loss and improve overall health.
- Patient Selection: Candidates for MGB should be carefully selected based on their medical history, BMI, and willingness to commit to lifelong dietary and lifestyle changes.
Vertical Banded Gastroplasty (VBG)
Definition:
Vertical Banded Gastroplasty (VBG), also known as stomach stapling, is a restrictive bariatric surgery designed to limit food intake by creating a small stomach pouch with a vertical staple line and a plastic band.
VBG aims to achieve weight loss by restricting the amount of food that can be consumed and slowing the passage of food from the pouch to the rest of the stomach.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Patients undergo comprehensive medical assessments, including physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, to evaluate overall health and suitability for surgery.
- Surgical Procedure: VBG is performed under general anesthesia and begins with the surgical creation of a small stomach pouch using surgical staples or sutures to partition the upper stomach from the lower portion.
- Placement of Vertical Band: A non-adjustable band made of mesh or other material is placed around the stomach pouch to maintain the size of the pouch and control food passage.
- Closure and Recovery: The procedure concludes with closure of incisions and post-operative monitoring to manage pain, monitor for complications, and initiate dietary progression.
Benefits:
- Effective Weight Loss: VBG can lead to significant and sustained weight loss by limiting food intake and promoting early satiety.
- Restrictive Nature: By creating a small stomach pouch and narrowing the passage of food, VBG helps patients consume smaller portions and reduce overall calorie intake.
- Preservation of Digestive Tract: Unlike malabsorptive procedures, VBG preserves the natural anatomy of the digestive tract, reducing the risk of nutritional deficiencies.
- Potential for Reversibility: While not commonly reversed, VBG theoretically allows for revision or conversion to other bariatric procedures if necessary for medical or weight loss reasons.
Considerations:
- Risk of Complications: Potential risks include staple line disruption, band erosion, or dilation of the stomach pouch requiring surgical intervention.
- Dietary Adherence: Long-term success with VBG requires strict adherence to dietary guidelines, including portion control, nutrient-dense foods, and avoidance of high-calorie, low-nutrient options.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular physical activity, behavioral counseling, and ongoing medical supervision are essential for optimizing weight loss outcomes and maintaining overall health.
- Patient Selection: Candidates for VBG should be carefully selected based on BMI, medical history, and commitment to lifelong dietary and lifestyle changes to achieve sustainable weight loss and improved health.
Gastric Band Removal Surgery
Definition:
Gastric Band Removal Surgery is a procedure performed to remove an existing adjustable gastric band from the stomach due to complications, inadequate weight loss, or patient preference for an alternative weight loss solution.
This surgical intervention may involve band removal only or may be followed by revision surgery to address underlying concerns or achieve desired weight loss outcomes.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Patients undergo comprehensive medical assessments, including review of prior surgical history, diagnostic tests, and consultations with bariatric specialists to determine the reasons for band removal and assess overall health status.
- Surgical Procedure: Gastric Band Removal is typically performed under general anesthesia and begins with making small incisions in the abdomen to access the gastric band and associated components.
- Band Removal: The surgeon carefully removes the adjustable gastric band, including any connecting tubing and the access port, while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues and structures.
- Post-removal Care: Following band removal, patients may undergo additional procedures such as gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, or undergo no further intervention based on individual health needs and weight loss goals.
Benefits:
- Resolution of Complications: Removal of a malfunctioning or problematic gastric band can resolve associated complications such as band slippage, erosion, or inadequate weight loss.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients may experience relief from symptoms related to the gastric band, including reflux, discomfort, or difficulty with eating and digestion.
- Flexibility for Future Options: Band removal provides flexibility for patients to consider alternative weight loss procedures or non-surgical options based on their health status and weight loss goals.
- Enhanced Surgical Outcomes: In cases requiring revision surgery, band removal allows for improved outcomes with subsequent procedures to achieve sustainable weight loss and improve overall health.
Considerations:
- Surgical Risks: Potential risks include bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding structures, or complications related to anesthesia.
- Post-operative Recovery: Patients may experience discomfort, temporary dietary restrictions, and gradual resumption of normal activities following band removal surgery.
- Patient Counseling: Comprehensive counseling is essential to educate patients on the potential benefits and risks of band removal, alternative weight loss options, and long-term strategies for maintaining weight loss and overall health.
- Individualized Care: Decisions regarding band removal and subsequent procedures should be personalized based on patient-specific factors, including medical history, BMI, and preferences for weight loss interventions.
Conversion from Gastric Band to Sleeve Gastrectomy
Definition:
Conversion from Gastric Band to Sleeve Gastrectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove an existing adjustable gastric band and convert the patient’s anatomy to a sleeve gastrectomy.
This conversion surgery may be indicated due to complications with the gastric band, inadequate weight loss, or patient preference for a more effective and permanent weight loss solution.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Patients undergo comprehensive medical assessments, including review of prior surgical history, diagnostic tests, and consultations with bariatric specialists to determine the reasons for conversion and assess overall health status.
- Surgical Procedure: Conversion surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and begins with making small incisions in the abdomen to access the gastric band and associated components.
- Band Removal: The surgeon carefully removes the adjustable gastric band, including any connecting tubing and the access port, while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues and structures.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: Following band removal, the surgeon performs a sleeve gastrectomy by removing a large portion of the stomach and creating a narrow, tube-shaped stomach (sleeve) to restrict food intake and promote weight loss.
- Closure and Recovery: The procedure concludes with closure of incisions and post-operative monitoring to manage pain, monitor for complications, and initiate dietary progression.
Benefits:
- Effective Weight Loss: Conversion to sleeve gastrectomy offers significant and sustainable weight loss by reducing stomach capacity and altering gut hormones to promote early satiety.
- Resolution of Band-related Complications: Removing the gastric band resolves associated complications such as band slippage, erosion, or inadequate weight loss.
- Metabolic Benefits: Sleeve gastrectomy improves metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia through weight loss and altered nutrient absorption.
- Long-term Success: Sleeve gastrectomy is associated with long-term weight loss maintenance and improvement in overall health outcomes compared to gastric banding alone.
Considerations:
- Surgical Risks: Potential risks include bleeding, infection, staple line leaks, or complications related to anesthesia.
- Nutritional Monitoring: Regular monitoring and supplementation of essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and folate are essential following sleeve gastrectomy to prevent deficiencies.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Long-term success requires adherence to dietary recommendations, regular physical activity, and ongoing medical supervision to optimize weight loss outcomes and maintain overall health.
- Patient Counseling: Comprehensive counseling is essential to educate patients on the benefits and risks of conversion surgery, expectations for weight loss, and strategies for achieving sustainable results.
Conversion from Gastric Band to Gastric Bypass
Definition:
Conversion from Gastric Band to Gastric Bypass is a surgical procedure performed to remove an existing adjustable gastric band and convert the patient’s anatomy to a gastric bypass.
This conversion surgery may be indicated due to complications with the gastric band, inadequate weight loss, or patient preference for a more effective and permanent weight loss solution.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Patients undergo comprehensive medical assessments, including review of prior surgical history, diagnostic tests, and consultations with bariatric specialists to determine the reasons for conversion and assess overall health status.
- Surgical Procedure: Conversion surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and begins with making small incisions in the abdomen to access the gastric band and associated components.
- Band Removal: The surgeon carefully removes the adjustable gastric band, including any connecting tubing and the access port, while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues and structures.
- Gastric Bypass: Following band removal, the surgeon performs a gastric bypass by creating a small stomach pouch and bypassing a portion of the small intestine to reduce calorie absorption and promote weight loss.
- Closure and Recovery: The procedure concludes with closure of incisions and post-operative monitoring to manage pain, monitor for complications, and initiate dietary progression.
Benefits:
- Effective Weight Loss: Conversion to gastric bypass offers significant and sustainable weight loss by restricting food intake and altering digestive processes to promote early satiety.
- Resolution of Band-related Complications: Removing the gastric band resolves associated complications such as band slippage, erosion, or inadequate weight loss.
- Metabolic Benefits: Gastric bypass improves metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia through weight loss and altered nutrient absorption.
- Long-term Success: Gastric bypass is associated with long-term weight loss maintenance and improvement in overall health outcomes compared to gastric banding alone.
Considerations:
- Surgical Risks: Potential risks include anastomotic leaks, internal herniation, nutritional deficiencies, or complications related to anesthesia.
- Nutritional Monitoring: Regular monitoring and supplementation of essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and folate are essential following gastric bypass to prevent deficiencies.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Long-term success requires adherence to dietary recommendations, regular physical activity, and ongoing medical supervision to optimize weight loss outcomes and maintain overall health.
- Patient Counseling: Comprehensive counseling is essential to educate patients on the benefits and risks of conversion surgery, expectations for weight loss, and strategies for achieving sustainable results.
Gastric Banding with Simultaneous Hiatal Hernia Repair
Definition:
Gastric Banding with Simultaneous Hiatal Hernia Repair is a combined surgical procedure performed to address both obesity-related issues and a hiatal hernia, a condition where part of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
This surgery involves placing an adjustable gastric band to aid weight loss and repairing the hiatal hernia to improve digestive function and reduce symptoms such as reflux and discomfort.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Patients undergo comprehensive medical assessments, including diagnostic tests and imaging studies, to evaluate the severity of the hiatal hernia, assess obesity-related health risks, and determine candidacy for combined surgery.
- Surgical Procedure: The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and begins with addressing the hiatal hernia. The surgeon repairs the hernia by repositioning the stomach and closing the opening in the diaphragm to prevent future herniation.
- Gastric Band Placement: Following hiatal hernia repair, the surgeon places an adjustable gastric band around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch that limits food intake and promotes weight loss.
- Post-operative Care: Patients are closely monitored following surgery to manage pain, assess for complications such as hernia recurrence or band-related issues, and initiate dietary and lifestyle modifications to support weight loss and recovery.
Benefits:
- Comprehensive Treatment: Addresses both obesity-related concerns and hiatal hernia to improve overall health outcomes and quality of life.
- Weight Loss: Gastric banding aids in significant and sustained weight loss by restricting food intake and promoting early satiety.
- Hiatal Hernia Resolution: Surgical repair of the hiatal hernia reduces symptoms such as reflux, heartburn, and discomfort associated with stomach herniation into the chest cavity.
- Long-term Health Benefits: Combined surgery offers long-term benefits by addressing underlying conditions contributing to obesity and gastrointestinal issues.
Considerations:
- Surgical Complexity: Combined surgery requires specialized expertise in both bariatric procedures and hernia repair techniques to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize risks.
- Post-operative Recovery: Patients may experience discomfort, dietary restrictions, and gradual resumption of normal activities following surgery.
- Nutritional Counseling: Comprehensive nutritional counseling is essential to support weight loss goals, prevent nutritional deficiencies, and promote healthy eating habits post-surgery.
- Patient Education: Detailed patient education is necessary to inform individuals about the benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of combined surgery, enabling them to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
Laparoscopic Gastric Banding with Plication
Definition:
Laparoscopic Gastric Banding with Plication combines two bariatric procedures: adjustable gastric banding and gastric plication.
Gastric plication involves folding and suturing the stomach to create a smaller stomach volume, complementing the restrictive effects of the gastric band.
This combined approach aims to enhance weight loss outcomes by further limiting food intake and promoting early satiety.
Steps Involved:
- Pre-operative Evaluation: Patients undergo comprehensive medical assessments, including diagnostic tests and nutritional counseling, to assess obesity-related health risks and determine candidacy for combined surgery.
- Surgical Procedure: The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and begins with laparoscopic placement of an adjustable gastric band around the upper stomach to create a small pouch that restricts food intake.
- Gastric Plication: Following gastric band placement, the surgeon performs gastric plication by folding and suturing the stomach to reduce its size and enhance the restrictive effects of the gastric band.
- Post-operative Care: Patients are closely monitored following surgery to manage pain, assess for complications such as band slippage or plication-related issues, and initiate dietary and lifestyle modifications to support weight loss and recovery.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Weight Loss: Combining gastric banding with gastric plication enhances weight loss outcomes by further restricting food intake and promoting early satiety.
- Metabolic Benefits: Improves metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia through significant weight loss and altered digestive processes.
- Long-term Success: Combined surgery offers sustained benefits by addressing multiple factors contributing to obesity and promoting healthy weight management.
- Customized Approach: Allows for customization of surgical techniques based on individual patient needs and health conditions to achieve optimal outcomes.
Considerations:
- Surgical Expertise: Combined surgery requires specialized skills in both gastric banding and gastric plication techniques to ensure safe and effective procedures.
- Post-operative Recovery: Patients may experience discomfort, dietary restrictions, and gradual recovery following surgery.
- Nutritional Support: Comprehensive nutritional counseling is essential to support weight loss goals, prevent nutritional deficiencies, and promote healthy eating habits post-surgery.
- Patient Education: Detailed patient education is necessary to inform individuals about the benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of combined surgery, empowering them to actively participate in their health and recovery process.
The prices of all the types of the gastric band procedure.
Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: The cost of LAGB in Dubai typically ranges from AED 50,000 to AED 80,000 (approximately $13,600 to $21,800 USD). This cost includes surgeon fees, anesthesia, hospital charges, and pre-operative consultations.
Additional Costs:
- Pre-operative Tests: Approximately AED 2,000 to AED 5,000 ($545 to $1,360 USD) for blood tests, imaging (like ultrasound or MRI), and cardiac evaluation.
- Adjustments: Post-operative adjustments to the band can cost around AED 3,000 to AED 5,000 ($820 to $1,360 USD) per session.
- Follow-up Visits: Regular follow-up visits for monitoring and adjustments are typically included in the initial package cost but may incur additional charges if more adjustments are needed.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: The cost of LAGB in Turkey ranges from TRY 30,000 to TRY 50,000 (approximately $2,500 to $4,200 USD). Turkey generally offers more competitive pricing for medical procedures compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Pre-operative Tests: Approximately TRY 1,000 to TRY 2,000 ($85 to $170 USD) for comprehensive tests including blood work, imaging, and consultations.
- Adjustments: Similar to Dubai, adjustments to the band can cost around TRY 500 to TRY 1,000 ($40 to $85 USD) per session.
- Follow-up Visits: Follow-up visits are usually included in the initial package, but additional costs may apply for extra adjustments or consultations.
Adjustable Gastric Balloon (AGB)
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: The cost of AGB in Dubai ranges from AED 30,000 to AED 50,000 (approximately $8,200 to $13,600 USD), covering insertion and removal of the balloon, surgeon fees, anesthesia, and hospital charges.
Additional Costs:
- Pre-operative Tests: Around AED 1,500 to AED 3,000 ($410 to $820 USD) for required tests such as blood work, endoscopy, and consultations.
- Follow-up Visits: Typically included in the initial package cost, additional consultations or balloon adjustments may incur extra charges.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: The cost of AGB in Turkey ranges from TRY 20,000 to TRY 35,000 (approximately $1,700 to $3,000 USD), which is generally more cost-effective compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Pre-operative Tests: Approximately TRY 800 to TRY 1,500 ($65 to $125 USD) for necessary tests and consultations.
- Follow-up Visits: Similar to Dubai, follow-up visits are usually included in the initial package, with additional costs for adjustments or consultations.
Gastric Band Revision Surgery
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Gastric band revision surgery in Dubai ranges from AED 60,000 to AED 100,000 (approximately $16,400 to $27,300 USD), depending on the complexity of the revision required and hospital charges.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Comprehensive pre-operative tests may cost around AED 3,000 to AED 6,000 ($820 to $1,640 USD) for evaluating the need for revision and overall health.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up visits and adjustments post-surgery may incur additional charges based on the extent of revision needed.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Gastric band revision surgery in Turkey ranges from TRY 40,000 to TRY 70,000 (approximately $3,300 to $5,900 USD), which is generally more cost-effective compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Pre-operative tests are typically more affordable in Turkey, costing approximately TRY 1,500 to TRY 3,000 ($125 to $250 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and adjustments are generally included in the initial package, with additional costs for extensive revisions.
Mini-Gastric Bypass (MGB)
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Mini-Gastric Bypass in Dubai ranges from AED 80,000 to AED 120,000 (approximately $21,800 to $32,700 USD), covering surgeon fees, hospital charges, anesthesia, and post-operative care.
Additional Costs:
- Pre-operative Tests: Comprehensive tests may cost around AED 2,000 to AED 5,000 ($545 to $1,360 USD) for evaluating candidacy and health status.
- Nutritional Supplements: Ongoing costs for vitamin and mineral supplements are necessary to prevent deficiencies post-MGB.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Mini-Gastric Bypass in Turkey ranges from TRY 50,000 to TRY 90,000 (approximately $4,200 to $7,600 USD), offering a more cost-effective option compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Pre-operative Tests: Diagnostic tests are generally more affordable, costing approximately TRY 1,000 to TRY 2,000 ($85 to $170 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and nutritional counseling are crucial for long-term success and may incur additional costs.
Vertical Banded Gastroplasty (VBG)
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Vertical Banded Gastroplasty in Dubai ranges from AED 70,000 to AED 100,000 (approximately $19,100 to $27,300 USD), covering surgeon fees, hospital charges, anesthesia, and pre-operative tests.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Pre-operative tests may cost around AED 2,000 to AED 4,000 ($545 to $1,090 USD), including blood work, imaging, and consultations.
- Follow-up Visits: Regular visits for monitoring and adjustments are essential for successful outcomes post-VBG.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Vertical Banded Gastroplasty in Turkey ranges from TRY 60,000 to TRY 100,000 (approximately $5,000 to $8,400 USD), providing a cost-effective option compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tests are generally more affordable, costing approximately TRY 1,500 to TRY 3,000 ($125 to $250 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and nutritional counseling are crucial for long-term success and may incur additional costs.
Gastric Band Removal Surgery
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Gastric Band Removal Surgery in Dubai ranges from AED 40,000 to AED 70,000 (approximately $10,900 to $19,100 USD), covering surgeon fees, hospital charges, anesthesia, and pre-operative tests.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Pre-operative tests may cost around AED 1,500 to AED 3,000 ($410 to $820 USD), including imaging and consultations.
- Follow-up Care: Monitoring and potential additional procedures post-removal should be considered in the financial plan.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Gastric Band Removal Surgery in Turkey ranges from TRY 30,000 to TRY 50,000 (approximately $2,500 to $4,200 USD), offering a cost-effective option compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tests are generally more affordable, costing approximately TRY 1,000 to TRY 2,000 ($85 to $170 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and potential revision surgeries are crucial for managing complications or achieving desired weight loss outcomes.
Conversion from Gastric Band to Sleeve Gastrectomy
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Conversion from Gastric Band to Sleeve Gastrectomy in Dubai ranges from AED 90,000 to AED 140,000 (approximately $24,500 to $38,200 USD), covering surgeon fees, hospital charges, anesthesia, and pre-operative tests.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Comprehensive tests may cost around AED 2,500 to AED 5,000 ($680 to $1,360 USD), including imaging, blood work, and consultations.
- Follow-up Care: Monitoring and potential adjustments post-surgery are necessary for achieving desired weight loss outcomes.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Conversion from Gastric Band to Sleeve Gastrectomy in Turkey ranges from TRY 70,000 to TRY 120,000 (approximately $5,900 to $10,100 USD), offering a more cost-effective option compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tests are generally more affordable, costing approximately TRY 1,500 to TRY 3,000 ($125 to $250 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and nutritional counseling are crucial for long-term success and may incur additional costs.
Conversion from Gastric Band to Gastric Bypass
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Conversion from Gastric Band to Gastric Bypass in Dubai ranges from AED 100,000 to AED 150,000 (approximately $27,300 to $40,900 USD), covering surgeon fees, hospital charges, anesthesia, and pre-operative tests.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Comprehensive tests may cost around AED 3,000 to AED 6,000 ($820 to $1,640 USD), including imaging, blood work, and consultations.
- Follow-up Care: Monitoring and potential adjustments post-surgery are necessary for achieving desired weight loss outcomes.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Conversion from Gastric Band to Gastric Bypass in Turkey ranges from TRY 80,000 to TRY 130,000 (approximately $6,700 to $10,900 USD), offering a more cost-effective option compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tests are generally more affordable, costing approximately TRY 1,500 to TRY 3,000 ($125 to $250 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and nutritional counseling are crucial for long-term success and may incur additional costs.
Gastric Banding with Simultaneous Hiatal Hernia Repair
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Gastric Banding with Simultaneous Hiatal Hernia Repair in Dubai ranges from AED 100,000 to AED 150,000 (approximately $27,300 to $40,900 USD), covering surgeon fees, hospital charges, anesthesia, and pre-operative tests.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Comprehensive tests may cost around AED 3,000 to AED 6,000 ($820 to $1,640 USD), including imaging, blood work, and consultations.
- Follow-up Care: Monitoring and potential adjustments post-surgery are necessary for achieving desired weight loss outcomes.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Gastric Banding with Simultaneous Hiatal Hernia Repair in Turkey ranges from TRY 90,000 to TRY 140,000 (approximately $7,600 to $11,800 USD), offering a more cost-effective option compared to Dubai.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tests are generally more affordable, costing approximately TRY 2,000 to TRY 3,500 ($170 to $290 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and nutritional counseling are crucial for long-term success and may incur additional costs.
Laparoscopic Gastric Banding with Plication
Dubai:
- Procedure Cost: Laparoscopic Gastric Banding with Plication in Dubai ranges from AED 90,000 to AED 130,000 (approximately $24,500 to $35,400 USD), covering surgeon fees, hospital charges, anesthesia, and pre-operative tests.
Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Comprehensive tests may cost around AED 2,500 to AED 5,000 ($680 to $1,360 USD), including imaging, blood work, and consultations.
- Follow-up Care: Monitoring and potential adjustments post-surgery are necessary for achieving desired weight loss outcomes.
Turkey:
- Procedure Cost: Laparoscopic Gastric Banding with Plication in Turkey ranges from TRY 70,000 to TRY 120,000 (approximately $5,900 to $10,100 USD), offering a more cost-effective option compared to Dubai.
- Additional Costs:
- Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tests are generally more affordable, costing approximately TRY 1,500 to TRY 3,000 ($125 to $250 USD).
- Follow-up Care: Follow-up visits and nutritional counseling are crucial for long-term success and may incur additional costs.
Factors Affecting Gastric Band Surgery Costs
Medical Facilities and Expertise
In Dubai, renowned hospitals such as American Hospital Dubai and Medcare Hospital offer state-of-the-art facilities for gastric band procedures.
Turkey, on the other hand, boasts a growing reputation in medical tourism with hospitals like Acıbadem and Florence Nightingale.
Surgeon’s Expertise and Experience
The experience and reputation of the surgeon performing the procedure significantly influence costs. Dubai and Turkey both have highly skilled bariatric surgeons with varying fee structures based on their expertise and experience.
Pre-operative Evaluation
Costs often include pre-operative evaluations such as consultations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to assess the patient’s health and suitability for surgery.
Prices can differ based on the complexity and extent of these evaluations.
Post-operative Care and Follow-up
After surgery, patients require monitoring and follow-up appointments. Costs may vary depending on the frequency of visits and the included services such as nutritional counseling and adjustments to the gastric band.
Conclusion
Deciding where to undergo gastric band surgery involves weighing various factors including cost, quality of care, and personal preferences.
Both Dubai and Turkey offer distinct advantages, catering to different budgetary and medical needs.
By understanding the comprehensive breakdown of costs and considerations discussed in this guide, patients can make well-informed decisions to achieve their weight loss goals effectively and safely.
Whether you choose Dubai or Turkey for your gastric band procedure, prioritize your health and safety above all else.
Consult with qualified healthcare professionals to discuss your options thoroughly and ensure a successful outcome.
Make your decision confidently armed with the knowledge gained from this detailed comparison of costs and considerations.

