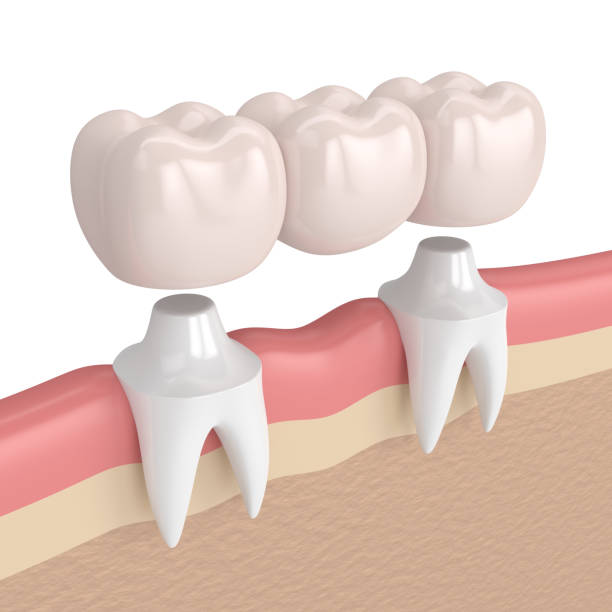
In the realm of dental healthcare, understanding the nuances of cost differentials for procedures like dental bridges between various countries plays a pivotal role in decision-making for patients.
This expansive article delves deeply into the intricate details of pricing variations between Qatar and Turkey for dental bridge procedures, offering a comprehensive analysis to aid prospective patients in making well-informed choices.

Overview of Dental Bridges
Dental bridges serve as crucial prosthetic devices used to replace missing teeth by bridging the gap between natural teeth or dental implants. They play a vital role not only in restoring aesthetics but also in maintaining proper dental function and preventing the shifting of adjacent teeth.
Types of Dental Bridge Procedures
Traditional Dental Bridge
Definition:
A traditional dental bridge is a common prosthetic device used to replace one or more missing teeth. It consists of one or more pontic (artificial teeth) anchored by dental crowns on either side of the gap.
These crowns are placed on the natural teeth or dental implants adjacent to the missing teeth, serving as abutments to support the bridge.
Details of Traditional Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Preparation: The procedure begins with the preparation of the abutment teeth. These adjacent teeth are reshaped by removing a portion of their enamel to make room for the dental crowns that will support the bridge. Impressions (molds) of the prepared teeth are then taken to ensure a precise fit of the bridge.
- Fabrication: A dental laboratory fabricates the bridge based on the impressions taken. The bridge is custom-made to match the shape, size, and color of the patient’s natural teeth, ensuring a seamless blend with the rest of the smile.
- Temporary Bridge: While the permanent bridge is being fabricated, a temporary bridge may be placed to protect the exposed teeth and gums.
- Placement: During a subsequent visit, the temporary bridge is removed, and the permanent bridge is carefully fitted and adjusted to ensure proper bite alignment and comfort. Once the fit is confirmed, the bridge is permanently cemented into place.
Benefits of Traditional Dental Bridge:
- Provides a stable and durable solution for replacing missing teeth.
- Restores the ability to chew and speak properly.
- Prevents neighboring teeth from shifting out of position.
- Enhances the aesthetic appearance of the smile by filling in gaps.
Considerations for Traditional Dental Bridge:
- Requires the reshaping of adjacent teeth, which may weaken them.
- Longevity of the bridge depends on oral hygiene practices and the health of supporting teeth.
- May not be suitable if the adjacent teeth are weak or have large fillings.
Cantilever Dental Bridge
Definition:
A cantilever dental bridge is similar to a traditional bridge but is anchored on only one side of the gap, rather than both sides.
This type of bridge is used when there are adjacent teeth on only one side of the missing tooth or teeth.
Details of Cantilever Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Preparation: The procedure involves reshaping the adjacent tooth (or teeth) on one side of the gap to accommodate a dental crown that will serve as the support for the bridge.
- Fabrication and Placement: Similar to a traditional bridge, the bridge is custom-made based on impressions of the prepared teeth. It is then bonded or cemented onto the reshaped adjacent tooth, extending over the gap to replace the missing tooth or teeth.
Benefits of Cantilever Dental Bridge:
- Provides a fixed solution for replacing missing teeth when there are adjacent teeth on only one side of the gap.
- Restores proper chewing function and prevents adjacent teeth from shifting.
Considerations for Cantilever Dental Bridge:
- Places additional stress on the single supporting tooth, which may affect its long-term health.
- Not suitable for areas of the mouth that undergo significant biting or chewing pressure.
- Requires careful assessment of the supporting tooth’s strength and health.
Maryland Dental Bridge (Resin-Bonded Bridge)
Definition:
A Maryland dental bridge, also known as a resin-bonded bridge, is a conservative option used primarily for replacing missing front teeth.
It involves a metal or porcelain framework bonded to the backs of adjacent teeth, eliminating the need for extensive tooth preparation compared to traditional bridges.
Details of Maryland Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Preparation: Minimal reshaping of the adjacent teeth is required compared to traditional bridges, preserving more of the natural tooth structure.
- Framework and Bonding: A metal or porcelain framework with artificial teeth (pontics) is created and bonded to the backs of the adjacent teeth using a resin cement. This provides support for the bridge and secures it in place.
Benefits of Maryland Dental Bridge:
- Preserves the structure of adjacent teeth better than traditional bridges, as it requires minimal tooth preparation.
- Minimally invasive procedure with less impact on surrounding teeth.
- Suitable for replacing front teeth where the biting forces are lighter.
Considerations for Maryland Dental Bridge:
- May not be as strong as traditional bridges, particularly for replacing molars or teeth subjected to heavy chewing forces.
- Long-term success depends on the strength and durability of the resin bond.
- Not suitable for replacing multiple teeth or teeth in areas with significant biting pressure.
Implant-Supported Dental Bridge
Definition:
An implant-supported dental bridge utilizes dental implants as anchors instead of natural teeth.
This type of bridge is recommended when several adjacent teeth are missing or when the natural teeth adjacent to the gap are not strong enough to support a traditional bridge.
Details of Implant-Supported Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Implant Placement: The procedure begins with the surgical placement of dental implants (titanium posts) into the jawbone at the site of the missing teeth. The number of implants placed depends on the size and location of the gap.
- Healing Period: Following implant placement, a healing period of several months is required to allow the implants to integrate (fuse) with the jawbone through a process called osseointegration. This integration provides a stable foundation for the bridge.
- Bridge Fabrication and Placement: Once the implants have fully integrated with the jawbone, impressions of the dental implants are taken. A custom-made bridge, which includes pontics (artificial teeth) attached to crowns or a framework, is then fabricated. The bridge is securely attached to the implants using abutments, completing the restoration.
Benefits of Implant-Supported Dental Bridge:
- Provides a stable and long-lasting solution for replacing multiple missing teeth.
- Preserves bone structure and prevents bone loss that occurs with missing teeth.
- Restores full chewing function and maintains facial aesthetics.
Considerations for Implant-Supported Dental Bridge:
- Requires sufficient bone density and good oral health for successful implant placement and integration.
- Longer treatment timeline due to the healing period required for implants to osseointegrate.
- Generally more expensive than traditional bridges due to the cost of implants and surgical procedures involved.
Hybrid Dental Bridge (Implant-Supported Hybrid Bridge)
Definition:
A hybrid dental bridge combines the benefits of implant-supported bridges with a fixed denture appliance.
It is used when a patient is missing most or all of their teeth in an arch (either upper or lower jaw). This type of bridge provides a permanent, stable solution that restores both aesthetics and function.
Details of Hybrid Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Initial Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s oral health, including bone density and gum condition.
- Implant Placement: Dental implants are strategically placed in the jawbone to provide support for the hybrid bridge.
- Temporary Restoration: A temporary denture or bridge may be placed while the implants integrate with the jawbone.
- Final Restoration: Once osseointegration is complete, a custom-made hybrid bridge is fabricated. This bridge consists of a fixed denture appliance supported by multiple implants, providing a secure and natural-looking restoration.
Benefits of Hybrid Dental Bridge:
- Restores aesthetics and function for patients missing most or all teeth in an arch.
- Provides a stable and secure fit without the need for removable dentures.
- Prevents bone loss and maintains facial structure over time.
Considerations for Hybrid Dental Bridge:
- Requires a sufficient amount of bone for implant placement and integration.
- Initial cost may be higher than other types of dental bridges due to the complexity of the procedure.
- Regular maintenance and oral hygiene are crucial for long-term success.
Cantilever Resin-Bonded Bridge
Definition:
A cantilever resin-bonded bridge is a modification of the traditional resin-bonded bridge. It is used when there is only one adjacent tooth available for support on one side of the gap. This type of bridge is primarily used for replacing missing front teeth.
Details of Cantilever Resin-Bonded Bridge Procedure:
- Preparation: Minimal reshaping of the single adjacent tooth is required to accommodate the framework of the bridge.
- Framework and Bonding: A metal or porcelain framework with artificial teeth (pontics) is bonded to the single adjacent tooth using a resin cement, extending over the gap to replace the missing tooth.
Benefits of Cantilever Resin-Bonded Bridge:
- Provides a conservative solution with minimal impact on adjacent teeth.
- Suitable for replacing front teeth where the biting forces are lighter.
- Preserves more natural tooth structure compared to traditional bridges.
Considerations for Cantilever Resin-Bonded Bridge:
- Places additional stress on the single supporting tooth, which may affect its long-term health.
- Not suitable for areas of the mouth that undergo significant biting or chewing pressure.
- Longevity depends on the strength and durability of the resin bond.
Overdenture Dental Bridge
Definition:
An overdenture dental bridge is a removable prosthetic device that combines elements of a dental bridge and a denture. It is typically used when a patient is missing several teeth in an arch and requires a stable, yet removable, restoration.
Details of Overdenture Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Initial Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s oral health, including bone density and gum condition.
- Implant Placement (Optional): Dental implants may be placed in the jawbone to provide stability and retention for the overdenture bridge.
- Framework and Attachment: A metal or acrylic framework is custom-made to fit over the remaining natural teeth or dental implants. Artificial teeth (pontics) are attached to the framework to fill in the gaps caused by missing teeth.
- Attachment Mechanism: The overdenture bridge is designed to snap securely onto attachments (like locator attachments) on natural teeth or implants, providing stability and retention.
Benefits of Overdenture Dental Bridge:
- Provides a stable and secure restoration without the need for adhesives.
- Restores chewing function and enhances aesthetics.
- Offers flexibility as a removable option for cleaning and maintenance.
Considerations for Overdenture Dental Bridge:
- Requires sufficient bone density and good oral health for successful implant placement, if implants are used.
- Regular maintenance and hygiene are essential to prevent complications.
- Initial cost may be higher than traditional removable dentures due to the incorporation of implants and attachments.
Fixed-Fixed Dental Bridge
Definition:
A fixed-fixed dental bridge is a type of bridge where both ends of the bridge are fixed or cemented onto natural teeth or dental implants.
This design provides stability and distributes chewing forces evenly across the supporting teeth or implants.
Details of Fixed-Fixed Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Preparation: The adjacent natural teeth or dental implants are prepared by reshaping them to accommodate dental crowns.
- Impressions and Fabrication: Impressions of the prepared teeth or implants are taken to create a custom-fit bridge. A dental laboratory fabricates the bridge based on these impressions, ensuring a precise fit and optimal aesthetics.
- Placement: During a subsequent visit, the bridge is carefully fitted and adjusted to ensure proper bite alignment and comfort. Once the fit is confirmed, the bridge is permanently cemented into place.
Benefits of Fixed-Fixed Dental Bridge:
- Provides a stable and durable solution for replacing missing teeth.
- Restores chewing function and prevents neighboring teeth from shifting.
- Enhances the aesthetic appearance of the smile.
Considerations for Fixed-Fixed Dental Bridge:
- Requires reshaping of adjacent teeth or placement of implants, which may affect their long-term health.
- Longevity of the bridge depends on oral hygiene practices and the health of supporting teeth or implants.
- May not be suitable if adjacent teeth or implants are weak or have large restorations.
All-on-4 Dental Bridge
Definition:
The All-on-4 dental bridge is a full-arch restoration technique that utilizes four dental implants to support a fixed bridge for an entire upper or lower arch of teeth.
It is often recommended for patients who are missing all or most of their teeth in one arch and desire a permanent, stable solution.
Details of All-on-4 Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Initial Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s oral health, bone density, and anatomical considerations.
- Implant Placement: Four dental implants are strategically placed in the jawbone, typically at angles to maximize bone contact and minimize the need for bone grafting.
- Immediate Loading: In many cases, a temporary bridge can be attached to the implants on the same day as implant placement, allowing for immediate function and aesthetics.
- Final Restoration: After a healing period of several months to allow for osseointegration, a final fixed bridge is fabricated. The bridge consists of a full arch of artificial teeth attached to the implants, providing a permanent and natural-looking restoration.
Benefits of All-on-4 Dental Bridge:
- Provides a fixed and stable solution for replacing an entire arch of missing teeth.
- Restores chewing function, speech clarity, and facial aesthetics.
- Minimizes the need for bone grafting in many cases, due to the strategic placement of implants.
Considerations for All-on-4 Dental Bridge:
- Requires sufficient bone density and good oral health for successful implant placement and osseointegration.
- Initial cost may be higher than other types of dental bridges due to the number of implants and complexity of the procedure.
- Regular maintenance and hygiene are crucial for long-term success and durability of the restoration.
Removable Dental Bridge (Partial Denture)
Definition:
A removable dental bridge, often referred to as a partial denture, is a prosthetic appliance used to replace one or more missing teeth. Unlike fixed bridges, removable bridges can be taken out and cleaned daily by the patient.
Details of Removable Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Initial Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s oral health, including assessment of remaining natural teeth and gums.
- Impressions: Impressions of the remaining teeth and gums are taken to create a custom-fit partial denture.
- Framework and Attachment: The partial denture consists of a metal or acrylic framework with artificial teeth (pontics) attached. The framework is designed to clip onto the natural teeth adjacent to the gap, providing stability and retention.
Benefits of Removable Dental Bridge:
- Provides a non-invasive solution for replacing missing teeth.
- Allows for easy removal and cleaning, enhancing oral hygiene.
- Can be adjusted over time to accommodate changes in the mouth.
Considerations for Removable Dental Bridge:
- May not provide the same stability as fixed bridges or implant-supported bridges.
- Requires good oral hygiene practices to prevent gum disease and maintain oral health.
- May feel bulkier compared to fixed bridges, especially in the initial adjustment period.
Hybrid Removable Dental Bridge
Definition:
A hybrid removable dental bridge combines elements of a removable partial denture with the stability of dental implants.
This type of bridge is used when a patient is missing multiple teeth in an arch and desires a more secure and stable restoration than a traditional removable denture.
Details of Hybrid Removable Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Initial Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s oral health, bone density, and anatomical considerations.
- Implant Placement: Dental implants are surgically placed in the jawbone to provide support and retention for the hybrid bridge.
- Attachment Mechanism: The hybrid bridge consists of a removable denture appliance that is designed to snap securely onto attachments (like locator attachments) on the dental implants.
Benefits of Hybrid Removable Dental Bridge:
- Combines the benefits of a removable denture with the stability of dental implants.
- Provides improved chewing function and aesthetics compared to traditional removable dentures.
- Offers a secure fit without the need for adhesives.
Considerations for Hybrid Removable Dental Bridge:
- Requires sufficient bone density and good oral health for successful implant placement and osseointegration.
- Initial cost may be higher than traditional removable dentures due to the incorporation of implants.
- Regular maintenance and hygiene are essential for the longevity and function of the hybrid bridge.
Adhesive Dental Bridge (Maryland Bonded Bridge)
Definition:
An adhesive dental bridge, also known as a Maryland bonded bridge, is a conservative option used primarily for replacing missing front teeth.
It involves bonding artificial teeth (pontics) to the back of adjacent natural teeth using a resin cement.
Details of Adhesive Dental Bridge Procedure:
- Preparation: Minimal preparation of the adjacent natural teeth is required, preserving more of the tooth structure compared to traditional bridges.
- Framework and Bonding: A metal or porcelain framework with artificial teeth (pontics) is bonded to the backs of the adjacent teeth using a resin cement. This provides support for the bridge and secures it in place.
Benefits of Adhesive Dental Bridge:
- Preserves the structure of adjacent teeth better than traditional bridges, as it requires minimal tooth preparation.
- Minimally invasive procedure with less impact on surrounding teeth.
- Suitable for replacing front teeth where the biting forces are lighter.
Considerations for Adhesive Dental Bridge:
- May not be as strong as traditional bridges, particularly for replacing molars or teeth subjected to heavy chewing forces.
- Long-term success depends on the strength and durability of the resin bond.
- Not suitable for replacing multiple teeth or teeth in areas with significant biting pressure.
Prices of Dental Bridge Procedures in Qatar and Turkey
Traditional Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: AED 1,000 – 2,000 per tooth
- Fabrication of bridge: AED 3,000 – 6,000
- Placement and fitting: AED 1,500 – 3,000 per bridge
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: TRY 1,000 – 2,000 per tooth
- Fabrication of bridge: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
- Placement and fitting: TRY 1,500 – 3,000 per bridge
Cantilever Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: AED 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: AED 3,000 – 6,000
- Placement and fitting: AED 1,500 – 3,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: TRY 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
- Placement and fitting: TRY 1,500 – 3,000
Maryland Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: AED 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: AED 3,000 – 6,000
- Bonding and fitting: AED 1,500 – 3,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: TRY 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
- Bonding and fitting: TRY 1,500 – 3,000
Implant-Supported Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 300 – 700
- Dental implant (per implant): AED 5,000 – 10,000
- Implant-supported bridge fabrication: AED 15,000 – 30,000
- Placement and fitting: AED 2,000 – 5,000 per bridge
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 300 – 700
- Dental implant (per implant): TRY 5,000 – 10,000
- Implant-supported bridge fabrication: TRY 15,000 – 30,000
- Placement and fitting: TRY 2,000 – 5,000 per bridge
Hybrid Dental Bridge (Implant-Supported Hybrid Bridge)
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 300 – 700
- Dental implant (per implant): AED 5,000 – 10,000
- Hybrid bridge fabrication: AED 20,000 – 40,000
- Final placement and fitting: AED 3,000 – 6,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 300 – 700
- Dental implant (per implant): TRY 5,000 – 10,000
- Hybrid bridge fabrication: TRY 20,000 – 40,000
- Final placement and fitting: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
Cantilever Resin-Bonded Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and bonding: AED 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: AED 3,000 – 6,000
- Bonding and fitting: AED 1,500 – 3,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and bonding: TRY 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
- Bonding and fitting: TRY 1,500 – 3,000
Overdenture Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Preliminary impressions: AED 500 – 1,000
- Implant placement (if required): AED 5,000 – 10,000 per implant
- Overdenture fabrication: AED 10,000 – 20,000
- Attachment and fitting: AED 2,000 – 5,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Preliminary impressions: TRY 500 – 1,000
- Implant placement (if required): TRY 5,000 – 10,000 per implant
- Overdenture fabrication: TRY 10,000 – 20,000
- Attachment and fitting: TRY 2,000 – 5,000
Fixed-Fixed Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: AED 1,000 – 2,000 per tooth
- Fabrication of bridge: AED 3,000 – 6,000
- Placement and fitting: AED 1,500 – 3,000 per bridge
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and impressions: TRY 1,000 – 2,000 per tooth
- Fabrication of bridge: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
- Placement and fitting: TRY 1,500 – 3,000 per bridge
All-on-4 Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 300 – 700
- All-on-4 implant surgery (including implants): AED 50,000 – 80,000
- Provisional bridge: AED 10,000 – 20,000
- Final bridge fabrication: AED 30,000 – 50,000
- Placement and fitting: AED 5,000 – 10,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 300 – 700
- All-on-4 implant surgery (including implants): TRY 50,000 – 80,000
- Provisional bridge: TRY 10,000 – 20,000
- Final bridge fabrication: TRY 30,000 – 50,000
- Placement and fitting: TRY 5,000 – 10,000
Removable Dental Bridge (Partial Denture)
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Preliminary impressions: AED 500 – 1,000
- Fabrication of partial denture: AED 3,000 – 6,000
- Adjustment and fitting: AED 1,000 – 2,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Preliminary impressions: TRY 500 – 1,000
- Fabrication of partial denture: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
- Adjustment and fitting: TRY 1,000 – 2,000
Hybrid Removable Dental Bridge
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 300 – 700
- Implant placement (including implants): AED 50,000 – 80,000
- Hybrid bridge fabrication: AED 20,000 – 40,000
- Attachment and fitting: AED 3,000 – 6,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 300 – 700
- Implant placement (including implants): TRY 50,000 – 80,000
- Hybrid bridge fabrication: TRY 20,000 – 40,000
- Attachment and fitting: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
Adhesive Dental Bridge (Maryland Bonded Bridge)
Qatar:
- Consultation and assessment: AED 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and bonding: AED 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: AED 3,000 – 6,000
- Bonding and fitting: AED 1,500 – 3,000
Turkey:
- Consultation and assessment: TRY 200 – 500
- Tooth preparation and bonding: TRY 1,000 – 2,000
- Fabrication of bridge: TRY 3,000 – 6,000
- Bonding and fitting: TRY 1,500 – 3,000
Considerations for Patients
- When deciding between Qatar and Turkey for dental bridge procedures, patients should carefully consider the following factors:
- Quality and Reputation: Evaluating the qualifications, experience, and reputation of dentists and dental clinics in both countries.
- Travel Logistics: Assessing travel costs, visa requirements, transportation, and accommodation options, as well as language considerations.
- Post-Procedure Care: Understanding the availability of follow-up care, complications management, and the clinic’s responsiveness to patient needs.
- Cost vs. Value: Balancing the upfront cost of the dental bridge procedure with the overall quality of care and potential long-term benefits.
- Patient Reviews and Testimonials: Seeking feedback from other patients who have undergone dental treatments in Qatar or Turkey to gain insights into their experiences.
Factors Influencing the Price of Dental Bridge Procedures
Financial Factors:
Cost of Materials:
The choice of material for the dental bridge plays a crucial role in determining its cost. Common materials include porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM), all-ceramic (such as zirconia), and composite resin.
Each material varies in terms of durability, aesthetics, and cost. For instance, all-ceramic bridges tend to be more expensive due to their superior aesthetics and biocompatibility.
Laboratory Fees:
Dental bridges are custom-made in dental laboratories. The complexity of the restoration, the expertise of the technicians, and the quality of materials used by the laboratory can significantly impact the overall cost.
High-quality laboratories with skilled technicians may charge higher fees for their services.
Dental Practice Overheads:
The operational costs of dental practices, including rent, utilities, staff salaries, and equipment maintenance, contribute to the pricing of dental procedures.
Practices located in prime urban areas or upscale neighborhoods may have higher overhead costs, which are reflected in their treatment fees.
Geographical Location:
The location of the dental practice plays a pivotal role in determining treatment costs. Urban centers and regions with higher living standards generally have higher dental fees compared to rural areas.
Factors such as local economic conditions, cost of living, and competition among dental practices influence pricing variations across different locations.
Dentist’s Expertise and Reputation:
Experienced and highly skilled dentists often command higher fees for their services. Dentists who specialize in complex dental procedures, such as implant-supported bridges or cosmetic dentistry, may charge premium prices based on their expertise, reputation, and successful patient outcomes.
Insurance Coverage:
The extent of insurance coverage for dental bridge procedures varies among insurance plans and providers.
Some insurance policies may cover a portion of the cost of certain types of bridges, while others may require patients to bear the entire expense out-of-pocket.
Insurance coverage policies and reimbursement rates influence the financial burden on patients seeking dental treatment.
Social and Healthcare Factors:
Technological Advances:
Dental practices equipped with advanced technology and digital dental equipment may offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities, precision in treatment planning, and superior outcomes.
Investments in technologies such as CAD/CAM (computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing) systems for fabricating dental restorations can contribute to higher treatment costs due to the use of cutting-edge materials and techniques.
Regulatory Standards:
Compliance with stringent regulatory standards and guidelines for dental practices ensures patient safety, quality of care, and adherence to ethical practices.
Dental practices that invest in maintaining high standards of infection control, sterilization protocols, and patient comfort may reflect these investments in their pricing structure.
Patient Demand and Competition:
Market demand for specific dental services, along with competition among dental practices, influences pricing dynamics.
Practices in competitive markets may adjust their fees to attract and retain patients. Patient preferences for aesthetic outcomes, treatment convenience, and the reputation of dental providers contribute to the demand for specific types of dental bridges and subsequent pricing strategies.
Economic Conditions:
Economic factors such as inflation rates, currency fluctuations, and overall economic stability impact the cost of dental materials, equipment, and operational expenses for dental practices.
Economic downturns or fluctuations in disposable income levels may influence patient spending on elective dental procedures and affect pricing strategies adopted by dental providers.
Training and Education Costs:
Ongoing professional development and training for dental professionals to acquire advanced skills, stay updated with technological advancements, and maintain licensure requirements contribute to the overall cost structure of dental services.
Practices that invest in continuing education and training for their staff members may incorporate these costs into their service fees.
Patient Preferences and Expectations:
Patient preferences for treatment outcomes, including aesthetic considerations, functional improvements, and treatment durability, influence the choice of dental bridges and treatment modalities.
Patient consultations and treatment planning discussions with dentists focus on addressing individual preferences, expectations, and budget considerations to achieve optimal treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Healthcare System and Policies:
Variations in healthcare systems and policies across different countries or regions impact access to dental care, reimbursement rates for dental procedures, and government subsidies or incentives for oral health services.
Government-funded healthcare initiatives, public health programs, and insurance regulations play a role in determining patient affordability and the availability of dental treatment options.
Ethical Considerations:
Dental practices that prioritize ethical standards, transparency in pricing, informed consent, and patient education foster trust and accountability with patients.
Ethical considerations in dental care encompass fair pricing practices, honest communication regarding treatment options, and comprehensive patient-centered care approaches to ensure positive treatment experiences and long-term oral health outcomes.
Cultural and Social Norms:
Cultural attitudes towards dental health, oral hygiene practices, and aesthetic preferences influence the demand for specific dental treatments and the willingness of individuals to invest in dental care.
Societal norms regarding dental aesthetics, perceptions of oral health, and the value placed on maintaining a healthy smile impact patient decisions regarding elective dental procedures, including dental bridges.
Comprehensive Planning and Consultation
Making an informed decision about where to undergo a dental bridge procedure involves thorough planning and consultation.
Patients should research prospective dental clinics, review patient testimonials, and consult with dental professionals or medical tourism experts to ensure their chosen destination meets their expectations for quality, affordability, and overall patient experience.
Conclusion
Choosing between Qatar and Turkey for a dental bridge procedure requires careful consideration of various factors, including cost, quality of care, accessibility, and personal preferences.
Qatar offers high-quality healthcare with advanced facilities but at a higher cost, while Turkey provides cost-effective options without compromising on standards.
By understanding the detailed cost breakdown and factors influencing pricing in each country, patients can make informed decisions that align with their healthcare needs and financial considerations.
In conclusion, whether opting for Qatar’s premium healthcare infrastructure or Turkey’s affordable dental tourism opportunities, patients can find suitable options for dental bridge procedures by conducting thorough research and seeking guidance from dental professionals or medical tourism specialists.

